Epidermal growth factor increases the interaction between nucleolin and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K/poly(C) binding protein 1 complex to regulate the gastrin mRNA turnover
- PMID: 17928403
- PMCID: PMC2096583
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e07-04-0384
Epidermal growth factor increases the interaction between nucleolin and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K/poly(C) binding protein 1 complex to regulate the gastrin mRNA turnover
Abstract
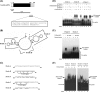
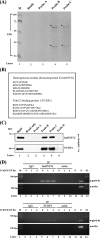
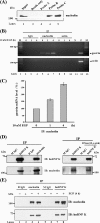
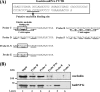
Gastrin, a gastrointestinal hormone responsible for gastric acid secretion, has been confirmed as a growth factor for gastrointestinal tract malignancies. High expression of gastrin mRNA was observed in pancreatic and colorectal cancer; however, the mechanism is unclear. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) was found to increase gastrin mRNA stability, indicating mRNA turnover regulation mechanism is involved in the control of gastrin mRNA expression. Using biotin-labeled RNA probe pull-down assay combined with mass spectrometry analysis, we identified the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP K) and poly(C) binding protein 1 (PCBP1) bound with the C-rich region in gastrin mRNA 3' untranslated region. Nucleolin bound with the AGCCCU motif and interacted with hnRNP K were also demonstrated. Under EGF treatment, we observed the amount of nucleolin interacting with hnRNP K and gastrin mRNA increased. Using small interfering RNA technology to define their functional roles, we found hnRNP K, PCBP1, and nucleolin were all responsible for stabilizing gastrin mRNA. Moreover, nucleolin plays a crucial role in mediating the increased gastrin mRNA stability induced by EGF signaling. Besides, we also observed hnRNP K/PCBP1 complex bound with the C-rich region in the gastrin mRNA increased nucleolin binding with gastrin mRNA. Finally, a novel binding model was proposed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-mediated stabilization of leukemia inhibitory factor (lif) mRNA: involvement of Nucleolin and PCBP1.Biochem J. 2017 Jul 3;474(14):2349-2363. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170051. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 28512205
-
The 3'-untranslated region of p21WAF1 mRNA is a composite cis-acting sequence bound by RNA-binding proteins from breast cancer cells, including HuR and poly(C)-binding protein.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jan 31;278(5):2937-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M208439200. Epub 2002 Nov 12. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12431987
-
Identification of mRNA binding proteins that regulate the stability of LDL receptor mRNA through AU-rich elements.J Lipid Res. 2009 May;50(5):820-31. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M800375-JLR200. Epub 2009 Jan 13. J Lipid Res. 2009. PMID: 19141871 Free PMC article.
-
Precision mechanics with multifunctional tools: how hnRNP K and hnRNPs E1/E2 contribute to post-transcriptional control of gene expression in hematopoiesis.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012 Jun;13(4):391-400. doi: 10.2174/138920312801619484. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012. PMID: 22708489 Review.
-
Control of mRNA translation and stability in haematopoietic cells: the function of hnRNPs K and E1/E2.Biol Cell. 2004 Aug;96(6):407-11. doi: 10.1016/j.biolcel.2004.03.010. Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15384226 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into the biology of IRES elements through riboproteomic approaches.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:458927. doi: 10.1155/2010/458927. Epub 2010 Feb 2. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20150968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced translation by Nucleolin via G-rich elements in coding and non-coding regions of target mRNAs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Oct;39(19):8513-30. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr488. Epub 2011 Jul 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21737422 Free PMC article.
-
HnRNPK/miR-223/FBXW7 feedback cascade promotes pancreatic cancer cell growth and invasion.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 21;8(12):20165-20178. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15529. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28423622 Free PMC article.
-
cAMP-mediated stimulation of tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA translation is mediated by polypyrimidine-rich sequences within its 3'-untranslated region and poly(C)-binding protein 2.Mol Pharmacol. 2009 Oct;76(4):872-83. doi: 10.1124/mol.109.057596. Epub 2009 Jul 20. Mol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19620256 Free PMC article.
-
HnRNPK maintains single strand RNA through controlling double-strand RNA in mammalian cells.Nat Commun. 2022 Aug 29;13(1):4865. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32537-0. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36038571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aghib D. F., Bishop J. M., Ottolenghi S., Guerrasio A., Serra A., Saglio G. A 3′ truncation of MYC caused by chromosomal translocation in a human T-cell leukemia increases mRNA stability. Oncogene. 1990;5:707–711. - PubMed
-
- Aly A., Shulkes A., Baldwin G. S. Gastrins, cholecystokinins and gastrointestinal cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2004;1704:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Audic Y., Hartley R. S. Post-transcriptional regulation in cancer. Biol. Cell. 2004;96:479–498. - PubMed
-
- Bevilacqua A., Ceriani M. C., Capaccioli S., Nicolin A. Post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression by degradation of messenger RNAs. J. Cell. Physiol. 2003;195:356–372. - PubMed
-
- Bomsztyk K., Denisenko O., Ostrowski J. hnRNP K: One protein multiple processes. Bioessays. 2004;26:629–638. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

