Deliberate termination of life of newborns with spina bifida, a critical reappraisal
- PMID: 17929034
- PMCID: PMC2092440
- DOI: 10.1007/s00381-007-0478-3
Deliberate termination of life of newborns with spina bifida, a critical reappraisal
Abstract
Objects: Deliberate termination of life of newborns (involuntary euthanasia) with meningomyelocele (MMC) is practiced openly only in The Netherlands. 'Unbearable and hopeless suffering' is the single most cited criterion for this termination, together with the notion that 'there are no other proper medical means to alleviate this suffering'. In this paper, both (and other) statements are questioned, also by putting them in a broader perspective.
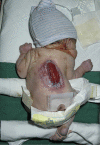
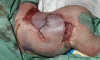
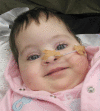
Methods: First, a historical overview of the treatment of newborns with MMC is presented, concentrating on the question of selection for treatment. Second, a thorough analysis is made of the criteria used for life termination. Third, a case of a newborn with a very severe MMC is presented as a 'reference case'.
Conclusion: 'Unbearable and hopeless suffering' cannot be applied to newborns with MMC. They are not 'terminally ill' and do have 'prospects of a future'. In these end-of-life decisions, 'quality of life judgments' should not be applied. When such a newborn is not treated, modern palliative care always will suffice in eliminating possible discomfort. There is no reason whatsoever for active life-termination of these newborns.
Figures
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '6744985', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6744985/'}]}
- Amacher AL, Wellington J (1984) Infantile hydrocephalus: long-term results of surgical therapy. Child Brain 11:217–229 - PubMed
-
- Anonymous (1979) Non-treatment of defective newborn babies. Lancet 1123–1124 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1017/S0012162203001518', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1017/s0012162203001518'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '14667073', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14667073/'}]}
- Barf HA (2003) Cognitive status of young adults with spina bifida. Dev Med Child Neurol 45:813–820 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1097/00004356-200403000-00006', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1097/00004356-200403000-00006'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15097169', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15097169/'}]}
- Barf HA, Verhoef M, Post MWM, Jennekens-Schinkel A, Gooskens RHJM, Mullaart RA, Prevo AJH (2004) Educational career and predictors of type of education in young adults with spina bifida. Int J Rehabil Res 27:45–52 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1007/s00381-004-1128-7', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-004-1128-7'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15952030', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15952030/'}]}
- Beeker TW, Scheers MM, Faber JAJ, Tulleken CAF (2006) Prediction of independence and intelligence at birth in meningomyelocele. Child’s Nerv Syst 22(1):33–37 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

