Method for lipidomic analysis: p53 expression modulation of sulfatide, ganglioside, and phospholipid composition of U87 MG glioblastoma cells
- PMID: 17929901
- PMCID: PMC4851466
- DOI: 10.1021/ac071413m
Method for lipidomic analysis: p53 expression modulation of sulfatide, ganglioside, and phospholipid composition of U87 MG glioblastoma cells
Abstract
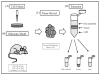
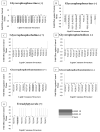
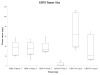
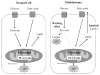
Lipidomics can complement genomics and proteomics by providing new insight into dynamic changes in biomembranes; however, few reports in the literature have explored, on an organism-wide scale, the functional link between nonenzymatic proteins and cellular lipids. Here, we report changes induced by adenovirus-delivered wild-type p53 gene and chemotherapy of U87 MG glioblastoma cells, a treatment known to trigger apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. We compare polar lipid changes in treated cells and control cells by use of a novel, sensitive method that employs lipid extraction, one-step liquid chromatography separation, high-resolution mass analysis, and Kendrick mass defect analysis. Nano-LC FT-ICR MS and quadrupole linear ion trap MS/MS analysis of polar lipids yields hundreds of unique assignments of glyco- and phospholipids at sub-ppm mass accuracy and high resolving power (m/Deltam50% = 200 000 at m/z 400) at 1 s/scan. MS/MS data confirm molecular structures in many instances. Sulfatides are most highly modulated by wild-type p53 treatment. The treatment also leads to an increase in phospholipids such as phosphatidyl inositols, phosphatidyl serines, phosphatidyl glycerols, and phosphatidyl ethanolamines. An increase in hydroxylated phospholipids is especially noteworthy. Also, a decrease in the longer chain gangliosides, GD1 and GM1b, is observed in wild-type p53 (treated) cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there is no conflict of interest with the data presented in this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Polar lipid remodeling and increased sulfatide expression are associated with the glioma therapeutic candidates, wild type p53 elevation and the topoisomerase-1 inhibitor, irinotecan.Glycoconj J. 2010 Jan;27(1):27-38. doi: 10.1007/s10719-009-9249-6. Epub 2009 Jun 26. Glycoconj J. 2010. PMID: 19557511
-
Highly sensitive localization analysis of gangliosides and sulfatides including structural isomers in mouse cerebellum sections by combination of laser microdissection and hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry with theoretically expanded multiple reaction monitoring.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2010 Oct 30;24(20):2957-65. doi: 10.1002/rcm.4716. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2010. PMID: 20872628
-
Targeted analysis of ganglioside and sulfatide molecular species by LC/ESI-MS/MS with theoretically expanded multiple reaction monitoring.J Lipid Res. 2008 Dec;49(12):2678-89. doi: 10.1194/jlr.D800038-JLR200. Epub 2008 Aug 14. J Lipid Res. 2008. PMID: 18703820
-
Screening of synthetic PDE-5 inhibitors and their analogues as adulterants: analytical techniques and challenges.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Jan;87:176-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.04.037. Epub 2013 May 6. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014. PMID: 23721687 Review.
-
New approach for glyco- and lipidomics--molecular scanning of human brain gangliosides by TLC-Blot and MALDI-QIT-TOF MS.J Neurochem. 2011 Mar;116(5):678-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07152.x. Epub 2011 Jan 19. J Neurochem. 2011. PMID: 21244424 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of plasma lipid biomarkers for prostate cancer by lipidomics and bioinformatics.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e48889. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048889. Epub 2012 Nov 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23152813 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Effects in the Liver of C57BL/6 Mice by Low Dose, High Energy, High Charge Irradiation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 30;22(21):11806. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111806. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769236 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple precursor ion scanning of gangliosides and sulfatides with a reversed-phase microfluidic chip and quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry.Anal Chem. 2012 Jul 17;84(14):5905-12. doi: 10.1021/ac300254d. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Anal Chem. 2012. PMID: 22697387 Free PMC article.
-
Lipidomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid by mass spectrometry-based methods.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2015 Jan;38(1):53-64. doi: 10.1007/s10545-014-9798-0. Epub 2014 Dec 9. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2015. PMID: 25488626 Review.
-
Integrative biological analysis for neuropsychopharmacology.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014 Jan;39(1):5-23. doi: 10.1038/npp.2013.156. Epub 2013 Jun 26. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23800968 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pelloski CE, Gilbert MR. Current treatment options in adult glioblastoma. US Oncolog Dis. 2007:105–109.
-
- Agnihotri S, Burrell KE, Wolf A, Jalali S, Hawkins C, Rutka JT, Zadeh G. Glioblastoma, a brief review of history, molecular genetics, animal models and novel therapeutic strategies. Archivum immunologiae et therapiae experimentalis. 2013;61(1):25–41. - PubMed
-
- Ohgaki H, Dessen P, Jourde B, Horstmann S, Nishikawa T, Di Patre PL, Burkhard C, Schuler D, Probst-Hensch NM, Maiorka PC, Baeza N, Pisani P, Yonekawa Y, Yasargil MG, Lutolf UM, Kleihues P. Genetic Pathways to Glioblastoma A Population-Based Study. Cancer Res. 2004;64(19):6892–6899. - PubMed
-
- Oertel J, von Buttlar E, Schroeder HW, Gaab MR. Prognosis of gliomas in the 1970s and today. Neurosurgical focus. 2005;18(4):e12–e12. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, Van Den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross G, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. New Eng J Med. 2005;352(10):987–996. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

