A league of their own: demographics, motivations and patterns of use of 1,955 male adult non-medical anabolic steroid users in the United States
- PMID: 17931410
- PMCID: PMC2131752
- DOI: 10.1186/1550-2783-4-12
A league of their own: demographics, motivations and patterns of use of 1,955 male adult non-medical anabolic steroid users in the United States
Abstract
Background: Rule violations among elite-level sports competitors and tragedies among adolescents have largely defined the issue of non-medical anabolic-androgenic steroid (NMAAS) use for the public and policy makers. However, the predominant and oft-ignored segment of the NMAAS community exists in the general population that is neither participating in competitive sports nor adolescent. A clearer profile of NMAAS users within the general population is an initial step in developing a full understanding of NMAAS use and devising appropriate policy and interventions. This survey sought to provide a more comprehensive profile of NMAAS users by accessing a large sample of user respondents from around the United States.
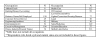
Methods: U.S.-based male NMAAS users (n = 1955) were recruited from various Internet websites dedicated to resistance training activities and use of ergogenic substances, mass emails, and print media to participate in a 291-item web-based survey. The Internet was utilized to provide a large and geographically diverse sample with the greatest degree of anonymity to facilitate participation.
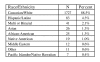
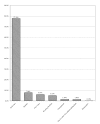
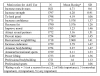
Results: The majority of respondents did not initiate AAS use during adolescence and their NMAAS use was not motivated by athletics. The typical user was a Caucasian, highly-educated, gainfully employed professional approximately 30 years of age, who was earning an above-average income, was not active in organized sports, and whose use was motivated by increases in skeletal muscle mass, strength, and physical attractiveness. These findings question commonly held views of the typical NMAAS user and the associated underlying motivations.
Conclusion: The focus on "cheating" athletes and at risk youth has led to ineffective policy as it relates to the predominant group of NMAAS users. Effective policy, prevention or intervention should address the target population(s) and their reasons for use while utilizing their desire for responsible use and education.
Figures







References
-
- National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) About anabolic steroid abuse. NIDA Notes. 2000;15 http://www.drugabuse.gov/NIDA_Notes/NN00index.html
-
- Todd T, Anabolic steroids. The gremlins of sport. J Sport Hist. 1987;14:87–107. - PubMed
-
- Yesalis CE, Courson SP, Wright J. History of anabolic steroid use in sport and exercise. In: Yesalis CE, editor. Anabolic Steroids in Sport and Exercise. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics; 1993. pp. 3–33.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
