XSTREAM: a practical algorithm for identification and architecture modeling of tandem repeats in protein sequences
- PMID: 17931424
- PMCID: PMC2233649
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-382
XSTREAM: a practical algorithm for identification and architecture modeling of tandem repeats in protein sequences
Abstract
Background: Biological sequence repeats arranged in tandem patterns are widespread in DNA and proteins. While many software tools have been designed to detect DNA tandem repeats (TRs), useful algorithms for identifying protein TRs with varied levels of degeneracy are still needed.
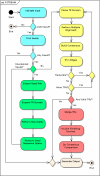
Results: To address limitations of current repeat identification methods, and to provide an efficient and flexible algorithm for the detection and analysis of TRs in protein sequences, we designed and implemented a new computational method called XSTREAM. Running time tests confirm the practicality of XSTREAM for analyses of multi-genome datasets. Each of the key capabilities of XSTREAM (e.g., merging, nesting, long-period detection, and TR architecture modeling) are demonstrated using anecdotal examples, and the utility of XSTREAM for identifying TR proteins was validated using data from a recently published paper.
Conclusion: We show that XSTREAM is a practical and valuable tool for TR detection in protein and nucleotide sequences at the multi-genome scale, and an effective tool for modeling TR domains with diverse architectures and varied levels of degeneracy. Because of these useful features, XSTREAM has significant potential for the discovery of naturally-evolved modular proteins with applications for engineering novel biostructural and biomimetic materials, and identifying new vaccine and diagnostic targets.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Search for Highly Divergent Tandem Repeats in Amino Acid Sequences.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 1;22(13):7096. doi: 10.3390/ijms22137096. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34281150 Free PMC article.
-
Pattern locator: a new tool for finding local sequence patterns in genomic DNA sequences.Bioinformatics. 2006 Dec 15;22(24):3099-100. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl551. Epub 2006 Nov 8. Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 17095514
-
Beyond tandem repeats: complex pattern structures and distant regions of similarity.Bioinformatics. 2002;18 Suppl 1:S31-7. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/18.suppl_1.s31. Bioinformatics. 2002. PMID: 12169528
-
Advancing genomic technologies and clinical awareness accelerates discovery of disease-associated tandem repeat sequences.Genome Res. 2022 Jan;32(1):1-27. doi: 10.1101/gr.269530.120. Epub 2021 Dec 29. Genome Res. 2022. PMID: 34965938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Statistical approaches to detecting and analyzing tandem repeats in genomic sequences.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2015 Mar 17;3:31. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2015.00031. eCollection 2015. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25853125 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding and identifying amino acid repeats.Brief Bioinform. 2014 Jul;15(4):582-91. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbt003. Brief Bioinform. 2014. PMID: 23418055 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of short tandem repeats genotyping tools in whole exome sequencing data.F1000Res. 2020 Mar 23;9:200. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.22639.1. eCollection 2020. F1000Res. 2020. PMID: 32665844 Free PMC article.
-
A refined genome phage display methodology delineates the human antibody response in patients with Chagas disease.iScience. 2021 May 15;24(6):102540. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102540. eCollection 2021 Jun 25. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34142048 Free PMC article.
-
Parallel Evolution of Ameloblastic scpp Genes in Bony and Cartilaginous Vertebrates.Mol Biol Evol. 2022 May 3;39(5):msac099. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msac099. Mol Biol Evol. 2022. PMID: 35535508 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic and Transcriptomic Analyses in the Slipper Snail Crepidula fornicata Uncover Shell Matrix Genes Expressed During Adult and Larval Biomineralization.Integr Org Biol. 2022 Aug 10;4(1):obac023. doi: 10.1093/iob/obac023. eCollection 2022. Integr Org Biol. 2022. PMID: 35968217 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

