A repressive role for prohibitin in estrogen signaling
- PMID: 17932104
- PMCID: PMC2234581
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2007-0400
A repressive role for prohibitin in estrogen signaling
Abstract
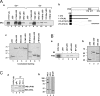
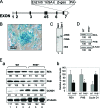
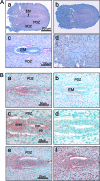
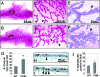
Nuclear receptor-mediated gene expression is regulated by corepressors and coactivators. In this study we demonstrate that prohibitin (PHB), a potential tumor suppressor, functions as a potent transcriptional corepressor for estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha). Overexpression of PHB inhibits ERalpha transcriptional activity, whereas depletion of endogenous PHB increases the expression of ERalpha target genes in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments demonstrate that PHB is associated with the estrogen-regulated pS2 promoter in the absence of hormone and dissociates after estradiol treatment. We demonstrate that PHB interacts with the repressor of estrogen receptor activity (REA), a protein related to PHB, to form heteromers and enhance the protein stability of both corepressors. Interestingly, the corepressor activity of PHB is cross-squelched by the coexpression of REA (and vice versa), suggesting that PHB and REA repress transcription only when they are not paired. We further demonstrate that coiled-coil domains located in the middle of PHB and REA are responsible for their heteromerization, stabilization, and cross-squelching actions. Finally, ablation of PHB function in the mouse results in early embryonic lethality, whereas mice heterozygous for the PHB null allele exhibit a hyperproliferative mammary gland phenotype. Our results indicate that PHB functions as a transcriptional corepressor for ERalpha in vitro and in vivo, and that its heteromerization with REA acts as a novel mechanism to limit its corepressor activity.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The silencing mediator of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptor (SMRT) corepressor is required for full estrogen receptor alpha transcriptional activity.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Sep;27(17):5933-48. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00237-07. Epub 2007 Jun 25. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17591692 Free PMC article.
-
Endocrine therapy resistance can be associated with high estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) expression and reduced ERalpha phosphorylation in breast cancer models.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006 Dec;13(4):1121-33. doi: 10.1677/erc.1.01257. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006. PMID: 17158758
-
Scaffold attachment factor SAFB1 suppresses estrogen receptor alpha-mediated transcription in part via interaction with nuclear receptor corepressor.Mol Endocrinol. 2006 Feb;20(2):311-20. doi: 10.1210/me.2005-0100. Epub 2005 Sep 29. Mol Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 16195251
-
Prohibitins role in cellular survival through Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK pathway.J Cell Physiol. 2014 Aug;229(8):998-1004. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24531. J Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24347342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prohibitin( PHB) roles in granulosa cell physiology.Cell Tissue Res. 2016 Jan;363(1):19-29. doi: 10.1007/s00441-015-2302-9. Cell Tissue Res. 2016. PMID: 26496733 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prohibitin: an unexpected role in sex dimorphic functions.Biol Sex Differ. 2016 Jun 24;7:30. doi: 10.1186/s13293-016-0083-9. eCollection 2016. Biol Sex Differ. 2016. PMID: 27347368 Free PMC article.
-
Progesterone-induced progesterone receptor membrane component 1 rise-to-decline changes are essential for decidualization.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2024 Feb 3;22(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12958-024-01188-9. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 38308254 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) through inhibiting interaction with prohibitins.iScience. 2023 Feb 28;26(4):106293. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106293. eCollection 2023 Apr 21. iScience. 2023. PMID: 36950117 Free PMC article.
-
LINC00478-derived novel cytoplasmic lncRNA LacRNA stabilizes PHB2 and suppresses breast cancer metastasis via repressing MYC targets.J Transl Med. 2023 Feb 13;21(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-03967-1. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36782197 Free PMC article.
-
Gonadectomy in Mito-Ob mice revealed a sex-dimorphic relationship between prohibitin and sex steroids in adipose tissue biology and glucose homeostasis.Biol Sex Differ. 2018 Aug 29;9(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s13293-018-0196-4. Biol Sex Differ. 2018. PMID: 30157935 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tsai MJ, O’Malley BW 1994 Molecular mechanisms of action of steroid/thyroid receptor superfamily members. Annu Rev Biochem 63:451–486 - PubMed
-
- Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG 2000 The coregulator exchange in transcriptional functions of nuclear receptors. Genes Dev 14:121–141 - PubMed
-
- Lonard DM, O’Malley BW 2006 The expanding cosmos of nuclear receptor coactivators. Cell 125:411–414 - PubMed
-
- O’Malley BW 2006 Molecular biology. Little molecules with big goals. Science 313:1749–1750 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

