Proteomic and functional analysis of Argonaute-containing mRNA-protein complexes in human cells
- PMID: 17932509
- PMCID: PMC2247381
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7401088
Proteomic and functional analysis of Argonaute-containing mRNA-protein complexes in human cells
Abstract
Members of the Argonaute (Ago) protein family associate with small RNAs and have important roles in RNA silencing. Here, we analysed Ago1- and Ago2-containing protein complexes in human cells. Separation of Ago-associated messenger ribonucleoproteins (mRNPs) showed that Ago1 and Ago2 reside in three complexes with distinct Dicer and RNA-induced silencing complex activities. A comprehensive proteomic analysis of Ago-containing mRNPs identified a large number of proteins involved in RNA metabolism. By using co-immunoprecipitation experiments followed by RNase treatment, we biochemically mapped interactions within Ago mRNPs. Using reporter assays and knockdown experiments, we showed that the putative RNA-binding protein RBM4 is required for microRNA-guided gene regulation.
Figures
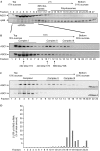
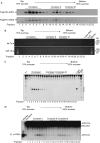

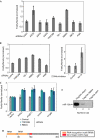
References
-
- Beitzinger M, Peters L, Zhu JY, Kremmer E, Meister G (2007) Identification of human microRNA targets from isolated Argonaute protein complexes. RNA Biol 4: e1–e9 - PubMed
-
- Eulalio A, Behm-Ansmant I, Izaurralde E (2007a) P bodies: at the crossroads of post-transcriptional pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8: 9–22 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

