Retinoic acid inducibility of the human PDGF-a gene is mediated by 5'-distal DNA motifs that overlap with basal enhancer and vitamin D response elements
- PMID: 17933214
- PMCID: PMC6042017
- DOI: 10.3727/000000007783991763
Retinoic acid inducibility of the human PDGF-a gene is mediated by 5'-distal DNA motifs that overlap with basal enhancer and vitamin D response elements
Abstract
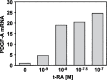
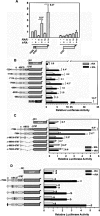
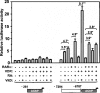
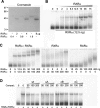
Retinoic acid (RA) upregulates expression of PDGF ligands and receptors in neonatal rat lung fibroblasts, a process likely to promote maturation of the lung alveolus and possibly microstructures of other organs. A mutational analysis of the gene encoding the PDGF-A ligand has identified a complex retinoic acid response element (RARE) located far upstream of the transcription start site, in a 5'-distal enhanceosome region previously shown to harbor basal and vitamin D-inducible enhancer activity. Maximal RA responsiveness (fourfold) was conferred by nucleotide sequence located between -7064 and -6787, with a variety of deletion and point mutations revealing the importance of at least three nuclear receptor half-sites within the enhancer region (-6851 to -6824), as well as nucleotides located further upstream. Recombinant human retinoic acid receptor/retinoid-X receptor heterodimers bound with high affinity and sequence specificity to multiple regions within the RARE, as demonstrated by electrophoretic mobility shift and DNase I footprinting assays. The addition of RARE activity to previously described functions of the 5'-distal enhanceosome underscores the importance of this region as a key integration point for regulatory control of PDGF-A expression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A 5'-distal element mediates vitamin D-inducibility of PDGF-A gene transcription.Growth Factors. 2003 Sep-Dec;21(3-4):151-60. doi: 10.1080/08977190310001636595. Growth Factors. 2003. PMID: 14708943
-
Different ligand responsiveness of human retinoic-acid-receptor beta-gene transcription in tumorigenic and non-tumorigenic cervical-carcinoma-derived cell lines is mediated through a large retinoic-acid-response domain.Int J Cancer. 1996 Jul 29;67(3):409-16. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19960729)67:3<409::AID-IJC16>3.0.CO;2-2. Int J Cancer. 1996. PMID: 8707417
-
Cytochrome P450RAI(CYP26) promoter: a distinct composite retinoic acid response element underlies the complex regulation of retinoic acid metabolism.Mol Endocrinol. 2000 Sep;14(9):1483-97. doi: 10.1210/mend.14.9.0518. Mol Endocrinol. 2000. PMID: 10976925
-
Retinoic acid induction of human cellular retinoic acid-binding protein-II gene transcription is mediated by retinoic acid receptor-retinoid X receptor heterodimers bound to one far upstream retinoic acid-responsive element with 5-base pair spacing.J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 2;269(35):22334-9. J Biol Chem. 1994. PMID: 8071361
-
A 5'-distal enhanceosome in the PDGF-A gene is activated in choriocarcinoma cells via ligand-independent binding of vitamin D receptor and constitutive jun kinase signaling.Oncogene. 2005 Apr 14;24(16):2654-66. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208336. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 15829977
Cited by
-
Aquaporin-4 Expression Switches from White to Gray Matter Regions during Postnatal Development of the Central Nervous System.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 3;24(3):3048. doi: 10.3390/ijms24033048. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769371 Free PMC article.
-
A Genome-Wide Search for Gene-Environment Effects in Isolated Cleft Lip with or without Cleft Palate Triads Points to an Interaction between Maternal Periconceptional Vitamin Use and Variants in ESRRG.Front Genet. 2018 Feb 26;9:60. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00060. eCollection 2018. Front Genet. 2018. PMID: 29535761 Free PMC article.
-
PDGF-A promoter and enhancer elements provide efficient and selective antineoplastic gene therapy in multiple cancer types.Cancer Gene Ther. 2009 Apr;16(4):298-309. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2008.92. Epub 2008 Nov 7. Cancer Gene Ther. 2009. PMID: 18989353 Free PMC article.
-
The calcitriol analogue EB1089 impairs alveolarization and induces localized regions of increased fibroblast density in neonatal rat lung.Exp Lung Res. 2008 May;34(4):155-82. doi: 10.1080/01902140801929325. Exp Lung Res. 2008. PMID: 18432454 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott B. D.; Best D. S.; Narotsky M. G. Teratogenic effects of retinoic acid are modulated in mice lacking expression of epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor-alpha. Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 73:204–217; 2005. - PubMed
-
- Al Jumaily W.; Bruce M. C. The postnatal age of rat lung fibroblasts influences G1/S phase transition in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 35:410–416; 1999. - PubMed
-
- Bastien J.; Rochette-Egly C. Nuclear retinoid receptors and the transcription of retinoid-target genes. Gene 328:1–16; 2004. - PubMed
-
- Betsholtz C. Insight into the physiological functions of PDGF through genetic studies in mice. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 15:215–228; 2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
