Cloning, expression, and functional analysis of rat liver cytosolic inorganic pyrophosphatase gene and characterization of its functional promoter
- PMID: 17933215
- PMCID: PMC6042020
- DOI: 10.3727/000000007783991754
Cloning, expression, and functional analysis of rat liver cytosolic inorganic pyrophosphatase gene and characterization of its functional promoter
Abstract
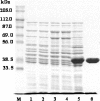
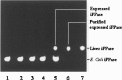
Inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi) is formed in several metabolic processes and its hydrolysis by the ubiquitously expressed enzyme inorganic pyrophosphatase (iPPase) is essential for the reactions to proceed in the direction of biosynthesis. Recently, we have reported differential expression and activity of cytosolic iPPase in rat liver with aging. In this article we report the cloning of the coding region of rat liver cytosolic iPPase gene in a bacterial expression vector, its expression, purification, and functional analysis by in-gel enzyme assay. SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis of this expressed protein revealed that its molecular weight (MW) is approximately 33 kDa, while in-gel assay showed that it is functionally active just as the liver cytosolic iPPase. We have determined the genomic organization of this gene by genome blast approach. We have also cloned and characterized its proximal approximate 1 kb functional promoter (-1009 to +82) by transient transfection and luciferase assay of different 5'-deleted iPPase promoter-luciferase constructs and also established its transcription start site by primer extension analysis, along with protein-DNA interaction studies for a few putative transcription factor binding sites.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Identification of Critical Elements for Regulation of Inorganic Pyrophosphatase (PPA1) in MCF7 Breast Cancer Cells.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 29;10(4):e0124864. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124864. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25923237 Free PMC article.
-
Age-dependent differential expression and activity of rat liver cytosolic inorganic pyrophosphatase gene.Biogerontology. 2007 Oct;8(5):517-25. doi: 10.1007/s10522-007-9094-6. Epub 2007 Apr 6. Biogerontology. 2007. PMID: 17415680
-
Age-dependent increased expression and activity of inorganic pyrophosphatase in the liver of male mice and its further enhancement with short- and long-term dietary restriction.Biogerontology. 2014 Feb;15(1):81-6. doi: 10.1007/s10522-013-9481-0. Epub 2013 Nov 24. Biogerontology. 2014. PMID: 24271717
-
High-throughput assay for inorganic pyrophosphatases using the cytosolic enzymes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and human as an example.Protein Expr Purif. 2000 Apr;18(3):303-9. doi: 10.1006/prep.1999.1189. Protein Expr Purif. 2000. PMID: 10733883
-
Purification and characterization of inorganic pyrophosphatase for in vitro RNA transcription.Biochem Cell Biol. 2022 Oct 1;100(5):425-436. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2022-0118. Epub 2022 Aug 4. Biochem Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35926232 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of Critical Elements for Regulation of Inorganic Pyrophosphatase (PPA1) in MCF7 Breast Cancer Cells.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 29;10(4):e0124864. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124864. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25923237 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baeuerle P. A.; Henkel T. Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 12:141–179; 1994. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle P. A.; Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: Ten years after. Cell 87:13–20; 1996. - PubMed
-
- Barkett M.; Gilmore T. D. Control of apoptosis by Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors. Oncogene 18:6910–6924; 1999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
