ATDB: a uni-database platform for animal toxins
- PMID: 17933766
- PMCID: PMC2238984
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm832
ATDB: a uni-database platform for animal toxins
Abstract
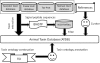
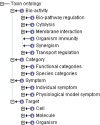
Venomous animals possess an arsenal of toxins for predation and defense. These toxins have great diversity in function and structure as well as evolution and therefore are of value in both basic and applied research. Recently, toxinomics researches using cDNA library sequencing and proteomics profiling have revealed a large number of new toxins. Although several previous groups have attempted to manage these data, most of them are restricted to certain taxonomic groups and/or lack effective systems for data query and access. In addition, the description of the function and the classification of toxins is rather inconsistent resulting in a barrier against exchanging and comparing the data. Here, we report the ATDB database and website which contains more than 3235 animal toxins from UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot and TrEMBL and related toxin databases as well as published literature. A new ontology (Toxin Ontology) was constructed to standardize the toxin annotations, which includes 745 distinct terms within four term spaces. Furthermore, more than 8423 TO terms have been manually assigned to 2132 toxins by trained biologists. Queries to the database can be conducted via a user-friendly web interface at http://protchem.hunnu.edu.cn/toxin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ATDB 2.0: A database integrated toxin-ion channel interaction data.Toxicon. 2010 Sep 15;56(4):644-7. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2010.05.013. Toxicon. 2010. PMID: 20677374
-
Animal Toxins: How is Complexity Represented in Databases?Toxins (Basel). 2010 Feb;2(2):262-82. doi: 10.3390/toxins2020262. Epub 2010 Feb 21. Toxins (Basel). 2010. PMID: 22069583 Free PMC article.
-
DEPD: a novel database for differentially expressed proteins.Bioinformatics. 2005 Sep 15;21(18):3694-6. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti580. Epub 2005 Jul 14. Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 16020467
-
Polypeptide toxins from animal venoms.Recent Pat DNA Gene Seq. 2007;1(3):200-6. doi: 10.2174/187221507782360254. Recent Pat DNA Gene Seq. 2007. PMID: 19075934 Review.
-
Molecular diversification in spider venoms: a web of combinatorial peptide libraries.Mol Divers. 2006 Nov;10(4):545-54. doi: 10.1007/s11030-006-9050-4. Epub 2006 Nov 10. Mol Divers. 2006. PMID: 17096075 Review.
Cited by
-
A sodium channel inhibitor ISTX-I with a novel structure provides a new hint at the evolutionary link between two toxin folds.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 13;6:29691. doi: 10.1038/srep29691. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27407029 Free PMC article.
-
Snake Venoms in Drug Discovery: Valuable Therapeutic Tools for Life Saving.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Sep 25;11(10):564. doi: 10.3390/toxins11100564. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31557973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
De novo assembly and annotation of Hyalomma dromedarii tick (Acari: Ixodidae) sialotranscriptome with regard to gender differences in gene expression.Parasit Vectors. 2018 May 24;11(1):314. doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-2874-9. Parasit Vectors. 2018. PMID: 29793520 Free PMC article.
-
Review on natural products databases: where to find data in 2020.J Cheminform. 2020 Apr 3;12(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s13321-020-00424-9. J Cheminform. 2020. PMID: 33431011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and functional diversity of acidic scorpion potassium channel toxins.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35154. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035154. Epub 2012 Apr 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22511981 Free PMC article.
References
-
- King GF. The wonderful world of spiders: preface to the special Toxicon issue on spider venoms. Toxicon. 2004;43:471–475. - PubMed
-
- Escoubas P, Rash L. Tarantulas: eight-legged pharmacists and combinatorial chemists. Toxicon. 2004;43:555–574. - PubMed
-
- Tedford HW, Sollod BL, Maggio F, King GF. Australian funnel-web spiders: master insecticide chemists. Toxicon. 2004;43:601–618. - PubMed
-
- Conticello SG, Gilad Y, Avidan N, Ben-Asher E, Levy Z, Fainzilber M. Mechanisms for evolving hypervariability: the case of conopeptides. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001;18:120–131. - PubMed
-
- Kozlov S, Malyavka A, McCutchen B, Lu A, Schepers E, Herrmann R, Grishin E. A novel strategy for the identification of toxinlike structures in spider venom. Proteins. 2005;59:131–140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

