Tuning of the outer hair cell motor by membrane cholesterol
- PMID: 17933870
- PMCID: PMC2679373
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M705078200
Tuning of the outer hair cell motor by membrane cholesterol
Abstract
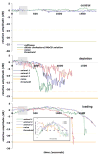
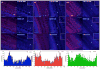
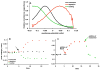
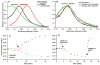
Cholesterol affects diverse biological processes, in many cases by modulating the function of integral membrane proteins. We observed that alterations of cochlear cholesterol modulate hearing in mice. Mammalian hearing is powered by outer hair cell (OHC) electromotility, a membrane-based motor mechanism that resides in the OHC lateral wall. We show that membrane cholesterol decreases during maturation of OHCs. To study the effects of cholesterol on hearing at the molecular level, we altered cholesterol levels in the OHC wall, which contains the membrane protein prestin. We show a dynamic and reversible relationship between membrane cholesterol levels and voltage dependence of prestin-associated charge movement in both OHCs and prestin-transfected HEK 293 cells. Cholesterol levels also modulate the distribution of prestin within plasma membrane microdomains and affect prestin self-association in HEK 293 cells. These findings indicate that alterations in membrane cholesterol affect prestin function and functionally tune the outer hair cell.
Figures
References
-
- Boesze-Battaglia K, Albert AD. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:20727–20730. - PubMed
-
- Chattopadhyay A, Jafurulla M, Kalipatnapu S, Pucadyil TJ, Harikumar KG. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;327:1036–1041. - PubMed
-
- Scanlon SM, Williams DC, Schloss P. Biochemistry. 2001;40:10507–10513. - PubMed
-
- Hinzpeter A, Fritsch J, Borot F, Trudel S, Vieu DL, Brouillard F, Baudoin-Legros M, Clain J, Edelman A, Ollero M. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:2423–2432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

