The Arabidopsis mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase MKK3 is upstream of group C mitogen-activated protein kinases and participates in pathogen signaling
- PMID: 17933903
- PMCID: PMC2174707
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.106.050039
The Arabidopsis mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase MKK3 is upstream of group C mitogen-activated protein kinases and participates in pathogen signaling
Abstract
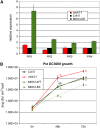
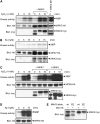
Although the Arabidopsis thaliana genome contains genes encoding 20 mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and 10 MAPK kinases (MAPKKs), most of them are still functionally uncharacterized. In this work, we analyzed the function of the group B MAPK kinase, MKK3. Transgenic ProMKK3:GUS lines showed basal expression in vascular tissues that was strongly induced by Pseudomonas syringae pv tomato strain DC3000 (Pst DC3000) infection but not by abiotic stresses. The growth of virulent Pst DC3000 was increased in mkk3 knockout plants and decreased in MKK3-overexpressing plants. Moreover, MKK3 overexpression lines showed increased expression of several PR genes. By yeast two-hybrid analysis, coimmunoprecipitation, and protein kinase assays, MKK3 was revealed to be an upstream activator of the group C MAPKs MPK1, MPK2, MPK7, and MPK14. Flagellin-derived flg22 peptide strongly activated MPK6 but resulted in poor activation of MPK7. By contrast, MPK6 and MPK7 were both activated by H(2)O(2), but only MPK7 activation was enhanced by MKK3. In agreement with the notion that MKK3 regulates the expression of PR genes, ProPR1:GUS expression was strongly enhanced by coexpression of MKK3-MPK7. Our results reveal that the MKK3 pathway plays a role in pathogen defense and further underscore the importance and complexity of MAPK signaling in plant stress responses.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade MKK3-MPK6 is an important part of the jasmonate signal transduction pathway in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2007 Mar;19(3):805-18. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.046581. Epub 2007 Mar 16. Plant Cell. 2007. PMID: 17369371 Free PMC article.
-
Riboflavin-Induced Disease Resistance Requires the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases 3 and 6 in Arabidopsis thaliana.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 7;11(4):e0153175. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153175. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27054585 Free PMC article.
-
A mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade module, MKK3-MPK6 and MYC2, is involved in blue light-mediated seedling development in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2014 Aug;26(8):3343-57. doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.128702. Epub 2014 Aug 19. Plant Cell. 2014. PMID: 25139007 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling through MAP kinase networks in plants.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2006 Aug 1;452(1):55-68. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2006.05.001. Epub 2006 May 24. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2006. PMID: 16806044 Review.
-
Modes of MAPK substrate recognition and control.Trends Plant Sci. 2015 Jan;20(1):49-55. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2014.09.006. Epub 2014 Oct 6. Trends Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 25301445 Review.
Cited by
-
Mining for protein S-sulfenylation in Arabidopsis uncovers redox-sensitive sites.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Oct 15;116(42):21256-21261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1906768116. Epub 2019 Oct 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31578252 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling Toward Reactive Oxygen Species-Scavenging Enzymes in Plants.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Feb 1;11:618835. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.618835. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33597960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitogen-Activated Protein (MAP) kinases in plant metal stress: regulation and responses in comparison to other biotic and abiotic stresses.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(6):7828-7853. doi: 10.3390/ijms13067828. Epub 2012 Jun 21. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22837729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uncovering molecular mechanisms involved in microbial volatile compounds-induced stomatal closure in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Mol Biol. 2023 Nov;113(4-5):143-155. doi: 10.1007/s11103-023-01379-9. Epub 2023 Nov 20. Plant Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37985583
-
Cellular Complexity in MAPK Signaling in Plants: Questions and Emerging Tools to Answer Them.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Nov 27;9:1674. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01674. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30538711 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Asai, T., Tena, G., Plotnikova, J., Willman, M.R., Chiu, W.L., Gomez-Gomez, L., Boller, T., Asubel, F.M., and Sheen, J. (2002). MAP kinase signaling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature 415 977–983. - PubMed
-
- Bögre, L., Calderini, O., Binarova, P., Mattauch, M., Till, S., Kiegerl, S., Jonak, C., Pollaschek, C., Barker, P., Huskisson, N.S., Hirt, H., and Heberle-Bors, E. (1999). A MAP kinase is activated late in plant mitosis and becomes localized to the plane of cell division. Plant Cell 11 101–113. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bradford, M.M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72 248–254. - PubMed
-
- Browse, J. (2005). Jasmonate: An oxylipin signal with many roles in plants. Vitam. Horm. 72 431–456. - PubMed
-
- Cardinale, F., Jonak, C., Ligterink, W., Niehaus, K., Boller, T., and Hirt, H. (2000). Differential activation of four specific MAPK pathways by distinct elicitors. J. Biol. Chem. 275 36734–36740. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

