Role of iron in human serum resistance of the clinical and environmental Vibrio vulnificus genotypes
- PMID: 17933938
- PMCID: PMC2168077
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01551-07
Role of iron in human serum resistance of the clinical and environmental Vibrio vulnificus genotypes
Erratum in
- Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008 May;74(10):3322
Abstract
We recently reported a simple PCR procedure that targets a sequence variation of the virulence-correlated gene locus vcg. It was found that 90% of all clinical isolates possessed the vcgC sequence variant, while 93% of all environmental isolates possessed the vcgE sequence variant. Here we report that the clinical genotype of Vibrio vulnificus is significantly better able to survive in human serum than is the environmental genotype. The presence of a siderophore-encoding gene, viuB, influenced serum survivability among all isolates of V. vulnificus tested. Those strains positive for viuB (all C-type strains but very few E-type strains) showed greater serum survivability than those lacking viuB (most E-type strains). The addition of iron (in the form of ferric ammonium citrate) to human serum restored the survival of E-type strains lacking viuB to levels not significantly different from those of C-type and E-type strains that possess viuB. These findings suggest that viuB may dictate serum survival in both C- and E-type strains of V. vulnificus and may explain why some strains (C- and E-type strains) are pathogenic and others (predominately E-type strains) are not. Additionally, C-type strains exhibited a cross-protective response against human serum, not exhibited by E-type strains, after incubation under nutrient and osmotic downshift conditions that mimicked estuarine waters. This suggests that the nutrient/osmotic environment may influence the survival of V. vulnificus following entry into the human body, leading to selection of the C genotype over the E genotype.
Figures

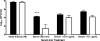


References
-
- Brennt, D. E., A. C. Writhe, S. K. Dutta, and J. G. Morris, Jr. 1991. Growth of Vibrio vulnificus in serum from alcoholics: association with high transferring iron saturation. J. Infect. Dis. 164:1030-1032. - PubMed
-
- Bullen, J. J., P. B. Spalding, C. G. Ward, and J. M. Gutteridge. 1991. Hemochromatosis, iron and septicemia caused by Vibrio vulnificus. Arch. Intern. Med. 151:1606-1609. - PubMed
-
- Hor, L.-I., T.-T. Chang, and S.-T. Wang. 1999. Survival of Vibrio vulnificus in whole blood from patients with chronic liver diseases: association with phagocytosis by neutrophils and serum ferritin levels. J. Infect. Dis. 179:275-278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

