Identification of a malate chemoreceptor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by screening for chemotaxis defects in an energy taxis-deficient mutant
- PMID: 17933940
- PMCID: PMC2168054
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01898-07
Identification of a malate chemoreceptor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by screening for chemotaxis defects in an energy taxis-deficient mutant
Abstract
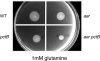
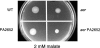
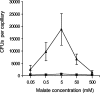
We found that a robust energy taxis response mediated by the Aer receptor can sometimes mask chemotaxis mediated by other methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins (MCPs) in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. We identified PA2652 as a chemoreceptor for malate by screening aer mcp double mutants by using swarm plate assays.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The activity of the C4-dicarboxylic acid chemoreceptor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is controlled by chemoattractants and antagonists.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 1;8(1):2102. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20283-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29391435 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Pseudomonas fluorescens chemotaxis sensory proteins for malate, succinate, and fumarate, and their involvement in root colonization.Microbes Environ. 2014;29(4):413-9. doi: 10.1264/jsme2.ME14128. Epub 2014 Dec 10. Microbes Environ. 2014. PMID: 25491753 Free PMC article.
-
Two different Pseudomonas aeruginosa chemosensory signal transduction complexes localize to cell poles and form and remould in stationary phase.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Jul;61(1):106-18. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05218.x. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16824098
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a model microorganism for investigation of chemotactic behaviors in ecosystem.J Biosci Bioeng. 2008 Jul;106(1):1-7. doi: 10.1263/jbb.106.1. J Biosci Bioeng. 2008. PMID: 18691523 Review.
-
Chemotaxis and flagellar genes of Chromobacterium violaceum.Genet Mol Res. 2004 Mar 31;3(1):92-101. Genet Mol Res. 2004. PMID: 15100991 Review.
Cited by
-
High-Affinity Chemotaxis to Histamine Mediated by the TlpQ Chemoreceptor of the Human Pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa.mBio. 2018 Nov 13;9(6):e01894-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01894-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 30425146 Free PMC article.
-
ChpC controls twitching motility-mediated expansion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in response to serum albumin, mucin and oligopeptides.Microbiology (Reading). 2020 Jul;166(7):669-678. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000911. Microbiology (Reading). 2020. PMID: 32478653 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging and analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa swarming and rhamnolipid production.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Dec;77(23):8310-7. doi: 10.1128/AEM.06644-11. Epub 2011 Oct 7. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21984238 Free PMC article.
-
Cytosine chemoreceptor McpC in Pseudomonas putida F1 also detects nicotinic acid.Microbiology (Reading). 2014 Dec;160(Pt 12):2661-2669. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.081968-0. Epub 2014 Oct 7. Microbiology (Reading). 2014. PMID: 25294107 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering Bacterial Chemorepulsion: The Complex Response of Microbes to Environmental Stimuli.Microorganisms. 2024 Aug 18;12(8):1706. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12081706. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39203548 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adler, J. 1973. A method for measuring chemotaxis and use of the method to determine optimum conditions for chemotaxis by Escherichia coli. J. Gen. Microbiol. 74:77-91. - PubMed
-
- Alexandre, G., S. Greer-Phillips, and I. B. Zhulin. 2004. Ecological role of energy taxis in microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 28:113-126. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez, C. 2007. Responses to low oxygen and energy taxis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Ph.D. thesis. University of Iowa, Iowa City.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

