Type III secretion systems and disease
- PMID: 17934073
- PMCID: PMC2176049
- DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00013-07
Type III secretion systems and disease
Abstract
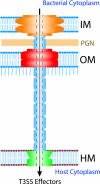
Type III secretion systems (T3SSs) are complex bacterial structures that provide gram-negative pathogens with a unique virulence mechanism enabling them to inject bacterial effector proteins directly into the host cell cytoplasm, bypassing the extracellular milieu. Although the effector proteins vary among different T3SS pathogens, common pathogenic mechanisms emerge, including interference with the host cell cytoskeleton to promote attachment and invasion, interference with cellular trafficking processes, cytotoxicity and barrier dysfunction, and immune system subversion. The activity of the T3SSs correlates closely with infection progression and outcome, both in animal models and in human infection. Therefore, to facilitate patient care and improve outcomes, it is important to understand the T3SS-mediated virulence processes and to target T3SSs in therapeutic and prophylactic development efforts.
Figures

References
-
- Abrahams, G. L., P. Muller, and M. Hensel. 2006. Functional dissection of SseF, a type III effector protein involved in positioning the salmonella-containing vacuole. Traffic 7:950-965. - PubMed
-
- Aepfelbacher, M. 2004. Modulation of Rho GTPases by type III secretion system translocated effectors of Yersinia. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 152:65-77. - PubMed
-
- Alto, N. M., F. Shao, C. Lazar, R. Brost, G. Chua, S. Mattoo, S. McMahon, P. Ghosh, T. Hughes, C. Boone, and J. Dixon. 2006. Identification of a bacterial type III effector family with G protein mimicry functions. Cell 124:133-145. - PubMed
-
- Arbibe, L., D. Kim, E. Batsche, T. Pedron, B. Mateescu, C. Muchardt, C. Parsot, and P. Sansonetti. 2007. An injected bacterial effector targets chromatin access for transcription factor NF-kappaB to alter transcription of host genes involved in immune responses. Nat. Immunol. 8:47-56. - PubMed
-
- Bertelsen, L., G. Paesold, S. Marcus, B. Finlay, L. Eckmann, and K. Barrett. 2004. Modulation of chloride secretory responses and barrier function of intestinal epithelial cells by the Salmonella effector protein SigD. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 287:C939-C948. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

