Systemic lupus erythematosus: new molecular targets
- PMID: 17934100
- PMCID: PMC2095294
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2007.078493
Systemic lupus erythematosus: new molecular targets
Abstract
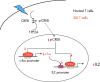
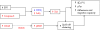
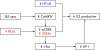
T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus exhibit a notable array of defects that probably contribute to the origin and development of the disease. Such abnormalities include an abnormal response to stimulation, aberrant expression of molecules that play key roles in intracellular signalling pathways, altered transcription factor activation and binding, and skewed gene expression. The combination of these alterations leads the cell to the expression of a particular phenotype that intense research has gradually uncovered over the last years. The aim of this article is to review the findings that have allowed us to better understand the behaviour of the lupus T cell and highlight the molecules that represent potential therapeutic targets.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Similar articles
-
[Interleukin-2 signaling pathway regulating molecules in systemic lupus erythematosus].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016 Dec 18;48(6):1100-1104. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016. PMID: 27987522 Review. Chinese.
-
Identification of microRNA-31 as a novel regulator contributing to impaired interleukin-2 production in T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Nov;64(11):3715-25. doi: 10.1002/art.34596. Arthritis Rheum. 2012. PMID: 22736314
-
Novel molecular targets in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus.Autoimmun Rev. 2008 Jan;7(3):256-61. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2007.11.020. Epub 2007 Dec 4. Autoimmun Rev. 2008. PMID: 18190888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methods and protocols to study T cell signaling abnormalities in human systemic lupus erythematosus.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;900:25-60. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-720-4_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22933064
-
How signaling and gene transcription aberrations dictate the systemic lupus erythematosus T cell phenotype.Trends Immunol. 2008 Mar;29(3):110-5. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2007.12.003. Epub 2008 Feb 4. Trends Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18249583 Review.
Cited by
-
Defective in vitro IL-2 production in lupus is an early but secondary event paralleling disease activity: evidence from the murine parent-into-F1 model supports staging of IL-2 defects in human lupus.Autoimmunity. 2010 Feb;43(1):23-31. doi: 10.3109/08916930903374808. Autoimmunity. 2010. PMID: 20001649 Free PMC article.
-
The catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2Ac) promotes DNA hypomethylation by suppressing the phosphorylated mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) kinase (MEK)/phosphorylated ERK/DNMT1 protein pathway in T-cells from controls and systemic lupus erythematosus patients.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 26;288(30):21936-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.467266. Epub 2013 Jun 17. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23775084 Free PMC article.
-
BAFF- and APRIL-targeted therapy in systemic autoimmune diseases.Inflamm Regen. 2016 Jul 21;36:6. doi: 10.1186/s41232-016-0015-4. eCollection 2016. Inflamm Regen. 2016. PMID: 29259679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Regulatory T-cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. IL-2 is decisive for loss of tolerance].Z Rheumatol. 2016 Apr;75(3):253-64. doi: 10.1007/s00393-016-0060-z. Z Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26975190 Review. German.
-
Genetic association of CD247 (CD3ζ) with SLE in a large-scale multiethnic study.Genes Immun. 2015 Mar;16(2):142-50. doi: 10.1038/gene.2014.73. Epub 2015 Jan 8. Genes Immun. 2015. PMID: 25569266 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parijs L V, Abbas A K. Homeostasis and self‐tolerance in the immune system: turning lymphocytes off. Science 1998280243–248. - PubMed
-
- Kyttaris V C, Juang Y T, Tsokos G C. Immune cells and cytokines in systemic lupus erythematosus: an update. Curr Opin Rheumatol 200517518–522. - PubMed
-
- Tsokos G C, Nambiar M P, Tenbrock K, Juang Y T. Rewiring the T‐cell: signaling defects and novel prospects for the treatment of SLE. Trends Immunol 200324259–263. - PubMed
-
- Vassilopoulos D, Kovacs B, Tsokos G C. TCR/CD3 complex‐mediated signal transduction pathway in T cells and T cell lines from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 19951552269–2281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical