S-adenosylmethionine as a biomarker for the early detection of lung cancer
- PMID: 17934114
- PMCID: PMC2562751
- DOI: 10.1378/chest.07-0622
S-adenosylmethionine as a biomarker for the early detection of lung cancer
Abstract
Background: S-Adenosylmethionine (AdoMet) is a major methyl donor for transmethylation reactions and propylamine donor for the biosynthesis of polyamines in biological systems, and therefore may play a role in lung cancer development. We hypothesized that AdoMet levels were elevated in patients with lung cancer and may prove useful as a biomarker for early lung cancer.
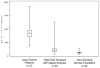
Methods: High-performance liquid chromatography was used to analyze plasma AdoMet levels in triplicate samples from 68 patients. This included 13 patients with lung cancer, 33 smokers with benign lung disease, and 22 healthy nonsmokers. The three groups of subjects were compared with respect to the distribution of demographic and disease characteristics and AdoMet levels. Distributions were examined using summary statistics and box plots, and nonparametric analysis of variance procedures.
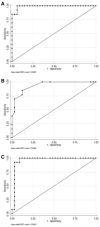
Results: Serum AdoMet levels were elevated in patients with lung cancer as compared to smokers with benign lung disorders and healthy nonsmokers. There were no significant correlations between AdoMet levels and tumor cell types, nodule size, or other demographic variables.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate that plasma levels of AdoMet are significantly elevated in patients with lung cancer. Plasma AdoMet levels may prove to be a useful tool for the diagnosis of early lung cancer, in combination with chest CT. Registered at: clinicaltrials.gov (NCT00301119).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Disturbed ratio of erythrocyte and plasma S-adenosylmethionine/S-adenosylhomocysteine in peripheral arterial occlusive disease.Atherosclerosis. 2001 Jan;154(1):147-54. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9150(00)00449-4. Atherosclerosis. 2001. PMID: 11137094
-
Plasma choline and betaine correlate with serum folate, plasma S-adenosyl-methionine and S-adenosyl-homocysteine in healthy volunteers.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2013 Mar 1;51(3):683-92. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2012-0302. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2013. PMID: 23095202
-
Stable-isotope dilution liquid chromatography-electrospray injection tandem mass spectrometry method for fast, selective measurement of S-adenosylmethionine and S-adenosylhomocysteine in plasma.Clin Chem. 2005 Aug;51(8):1487-92. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2004.046995. Epub 2005 May 26. Clin Chem. 2005. PMID: 15919880
-
S-adenosylmethionine in liver health, injury, and cancer.Physiol Rev. 2012 Oct;92(4):1515-42. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00047.2011. Physiol Rev. 2012. PMID: 23073625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The specific features of methionine biosynthesis and metabolism in plants.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Jun 23;95(13):7805-12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.13.7805. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9636232 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Resectable lung lesions malignancy assessment and cancer detection by ultra-deep sequencing of targeted gene mutations in plasma cell-free DNA.J Med Genet. 2019 Oct;56(10):647-653. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2018-105825. Epub 2019 Apr 13. J Med Genet. 2019. PMID: 30981987 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Epidemiology of lung cancer: Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines.Chest. 2013 May;143(5 Suppl):e1S-e29S. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-2345. Chest. 2013. PMID: 23649439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted metabolomics for serum amino acids and acylcarnitines in patients with lung cancer.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Jul;18(1):188-198. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7533. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31258653 Free PMC article.
-
Repressor logic modules assembled by rolling circle amplification platform to construct a set of logic gates.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 21;6:37477. doi: 10.1038/srep37477. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27869177 Free PMC article.
-
Study of the Relationship Between Serum Amino Acid Metabolism and Lymph Node Metastasis in Patients with Colorectal Cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Oct 13;13:10287-10296. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S273107. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 33116609 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Henschke CI, Yankelevitz D, Libby DM, et al. Survival of patients with stage I lung cancer detected on CT screening. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1763–1771. - PubMed
-
- Mulshine JL, Sullivan D. Lung cancer screening. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:2714–2720. - PubMed
-
- Hirsch FR, Franklin WA, Gazdar AF, et al. Early detection of lung cancer: clinical perspectives of recent advances in biology and radiology. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:5–22. - PubMed
-
- Bach PB, Jett JR, Pastorino U, et al. Computed tomography screening and lung cancer outcomes. JAMA. 2007;297:953–961. - PubMed
-
- Henschke CI, McCauley DI, Yankelevitz DF, et al. Early Lung Cancer Action Project: overall design and findings from baseline screening. Lancet. 1999;35:99–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

