Spontaneous renal artery dissection
- PMID: 17934571
- PMCID: PMC2002504
Spontaneous renal artery dissection
Abstract
Spontaneous renal artery dissection (SRAD) is a rare event, and thus may be a challenge for physicians to diagnose and treat. We report a case of SRAD in a healthy 56-year-old male who presented with flank pain, fever, and elevated white blood cell count. The patient was initially diagnosed with nephrolithiasis versus pyelonephritis and was admitted for observation. Multiple imaging modalities, including non-contrast computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with gadolinium, CT angiogram, and intraoperative angiogram, were used to make the final diagnosis of SRAD. The patient was treated with endovascular stent placement and is currently free of pain with normal laboratory values and blood pressure.
Keywords: Angiogram; Dissection; Endovascular stenting; Kidney; Renal artery.
Figures
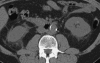

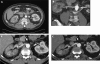
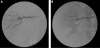
References
-
- Mudrick D, Arepally A, Geschwind JF. Spontaneous renal artery dissection: treatment with coil embolization. J Vasc & Int Rad. 2003;14(4):497–500. - PubMed
-
- Ramamoorthy SL, Vasquez JC, Taft PN. Nonoperative management of acute spontaneous renal artery dissection. Annals of Vasc Surg. 2002;16(2):157–162. - PubMed
-
- Beroniade V, Roy P, Froment D, Pison C. Primary renal artery dissection: presentation of two cases and brief review of the literature. Am J Nephrol. 1987;7:382–389. - PubMed
-
- LaCombe M. Isolated spontaneous dissection of the renal artery. J Vasc Surg. 2001;33:385–391. - PubMed
-
- Slavis SA, Hodge EE, Novick AC, Maatman T. Surgical treatment for isolated dissection of the renal artery. J Urol. 1990;144(2 Pt 1):233–237. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
