Oral insulin up-regulates Toll-like receptor 4 expression and enhances intestinal recovery following lipopolysaccharide-induced gut injury in a rat
- PMID: 17934814
- PMCID: PMC7102045
- DOI: 10.1007/s10620-007-9990-2
Oral insulin up-regulates Toll-like receptor 4 expression and enhances intestinal recovery following lipopolysaccharide-induced gut injury in a rat
Abstract
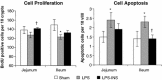
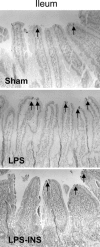
In the present study, we evaluated the protective effect of oral insulin (OI) on intestinal mucosa following lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal damage in a rat. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into three experimental groups: Sham rats, LPS-rats that were treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and LPS-INS rats that were treated with OI given in drinking water 72 h before and following injection of LPS. Intestinal structural changes, enterocyte proliferation, enterocyte apoptosis, and mucosal expression of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) were determined 24 h after the last LPS injection. LPS-INS animals showed a significantly greater bowel and mucosal weight in jejunum and ileum, mucosal DNA and protein in jejunum and ileum, villus height in ileum, crypt depth in jejunum and ileum, cell proliferation rates in jejunum, and significantly lower apoptotic index in ileum compared to LPS- animals. LPS rats demonstrated 50% increase in TLR4 expression in jejunum compared to sham animals. Treatment with OI resulted in a three-fold increase in TLR4 expression in jejunum, compared to LPS animals. In conclusion, OI improves intestinal recovery after LPS endotoxemia in a rat.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Oral glutamine prevents gut mucosal injury and improves mucosal recovery following lipopolysaccharide endotoxemia in a rat.J Surg Res. 2007 Dec;143(2):379-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2007.02.002. Epub 2007 Jun 14. J Surg Res. 2007. PMID: 17574581
-
Oral arginine reduces gut mucosal injury caused by lipopolysaccharide endotoxemia in rat.J Surg Res. 2004 Dec;122(2):256-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2004.07.004. J Surg Res. 2004. PMID: 15555626
-
Effect of oral insulin on diabetes-induced intestinal mucosal growth in rats.Dig Dis Sci. 2011 Sep;56(9):2566-74. doi: 10.1007/s10620-011-1654-6. Epub 2011 Mar 5. Dig Dis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21374061
-
Oral insulin enhances cell proliferation and decreases enterocyte apoptosis during methotrexate-induced mucositis in the rat.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008 Aug;47(2):115-22. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e31806008f1. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008. PMID: 18664860
-
Treatment with glutamine is associated with down-regulation of Toll-like receptor-4 and myeloid differentiation factor 88 expression and decrease in intestinal mucosal injury caused by lipopolysaccharide endotoxaemia in a rat.Clin Exp Immunol. 2008 Feb;151(2):341-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03571.x. Epub 2007 Dec 6. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18070149 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Berberine protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal injury in mice via alpha 2 adrenoceptor-independent mechanisms.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011 Nov;32(11):1364-72. doi: 10.1038/aps.2011.102. Epub 2011 Oct 3. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011. PMID: 21963898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deitch EA. The role of intestinal barrier failure and bacterial translocation in the development of systemic infection and multiple organ failure. Arch Surg. 1990;125:403–404. - PubMed
-
- Pugin J, Chevrolet JC. The intestine–liver–lung axis in septic syndrome. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1991;121:1538–1544. - PubMed
-
- Deitch EA (1993) Nutrition and the gut mucosal barrier. In: Daly J (ed) Current opinions in general surgery. Current Science, Philadelphia, PA, pp 85–91 - PubMed
-
- Mainous MR, Block EF, Deitch EA. Nutritional support of the gut: how and why. New Horiz. 1994;2:193–201. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

