Enhanced interferon-gamma secretion and antitumor activity of T-lymphocytes activated by dendritic cells loaded with glycoengineered myeloma antigens
- PMID: 17935669
- PMCID: PMC3178877
Enhanced interferon-gamma secretion and antitumor activity of T-lymphocytes activated by dendritic cells loaded with glycoengineered myeloma antigens
Abstract
Background: Immunotherapy is emerging as a promising cure for cancer. However, a severe problem in this area is the immune tolerance to tumor cells and tumor-associated antigens, as evidenced by the ability of cancer to escape immune surveillance. To overcome this problem this work examined the potential of improving the antigenicity of myeloma by metabolic engineering of its cell surface carbohydrate antigens (i.e., glycoengineering) and presentation of the modified tumor antigens by dendritic cells (DCs) to generate cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CTLs).
Methods: CD138+ myeloma cells were isolated from 11 multipe myeloma (MM) patients by the immunomagnetic bead method. The MM cells were treated with N-propionyl-D-mannosamine (ManNPr), a synthetic analog of N-acetyl-D-mannosamine (ManNAc), the natural biosynthetic precursor of N-acetyl sialic acid (NeuNAc), to express unnatural N-propionylated sialoglycans. The glycoengineered cells were then induced to apoptosis, and the apoptotic products were added to cultured functional DCs that could present the unnatural carbohydrate antigens to autologous T-lymphocytes.
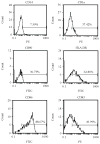
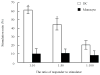
Results: It was found that the resultant DCs could activate CD4+ and CD8+ T-lymphocytes, resulting in increased expression of T cell surface markers, including CD8CD28 and CD4CD29. Moreover, upon stimulation by glycoengineered MM cells, these DC-activated T-lymphocytes could release significantly higher levels of IFN-gamma (P < 0.05). Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) assays further showed that the stimulated T-lymphocytes were cytotoxic to glycoengineered MM cells.
Conclusions: This work demonstrated that glycoengineered myeloma cells were highly antigenic and the CTLs induced by the DCs loaded with the unnatural myeloma antigens were specifically cytotoxic to the glycoengineered myeloma. This may provide a new strategy for overcoming the problem of immune tolerance for the development of effective immunotherapies for MM.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel cancer immunotherapy based on the combination of a synthetic carbohydrate-pulsed dendritic cell vaccine and glycoengineered cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2015 Mar 10;6(7):5195-203. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2908. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25760071 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of myeloma-specific T cells using dendritic cells loaded with MUC1- and hTERT- drived nonapeptides or myeloma cell apoptotic bodies.Neoplasma. 2010;57(5):455-64. doi: 10.4149/neo_2010_05_455. Neoplasma. 2010. PMID: 20568900
-
Tumor lysate-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in multiple myeloma: promising effector cells for immunotherapy.Blood. 2002 May 1;99(9):3280-5. doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.9.3280. Blood. 2002. PMID: 11964294
-
Dendritic cell biology and the application of dendritic cells to immunotherapy of multiple myeloma.Med Oncol. 2000 Feb;17(1):2-15. doi: 10.1007/BF02826210. Med Oncol. 2000. PMID: 10713654 Review.
-
Dendritic cell vaccines in the treatment of multiple myeloma: advances and limitations.Med Oncol. 2002;19(4):213-8. doi: 10.1385/MO:19:4:213. Med Oncol. 2002. PMID: 12512914 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel cancer immunotherapy based on the combination of a synthetic carbohydrate-pulsed dendritic cell vaccine and glycoengineered cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2015 Mar 10;6(7):5195-203. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2908. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25760071 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dalton WS, Bergsagel PL, Kuehl WM, Anderson KC. Multiple myeloma. Hematology (Am Soc Hematol Educ Program) 2001:157–177. - PubMed
-
- Chen CH, Wu TC. Experimental vaccine strategies for cancer immunotherapy. J Biomed Sci. 1998;5:231–252. - PubMed
-
- Mahal LK, Bertozzi CR. Engineered cell surfaces: fertile ground for molecular landscaping. Chem Biol. 1997;4:415–422. - PubMed
-
- Keppler OT, Stehling P, Herrmann M, Kayser H, Grunow D, Reutter W, et al. Biosynthetic modulation of sialic acid-dependent virus-receptor interactions of two primate polyoma viruses. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:1308–1314. - PubMed
-
- Luchansky SJ, Goon S, Bertozzi CR. Expanding the diversity of unnatural cell-surface sialic acids. Chem Biol Chem. 2004;5:371–374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

