Exaggerated glucagon-like peptide-1 and blunted glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide secretion are associated with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass but not adjustable gastric banding
- PMID: 17936091
- PMCID: PMC2134840
- DOI: 10.1016/j.soard.2007.08.004
Exaggerated glucagon-like peptide-1 and blunted glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide secretion are associated with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass but not adjustable gastric banding
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to measure the circulating levels of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP), and glucagon in patients who had undergone adjustable gastric banding (BND) or Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) to understand the differences in glucose and insulin regulation after these procedures.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study of 3 groups of women matched for age and body mass index: group 1, overweight controls (n = 13); group 2, BND (n = 10); and group 3, RYGB (n = 13). Venous blood was drawn with the patient in the fasted state and throughout a 3-hour period after a liquid meal.
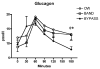
Results: The fasting glucose level was similar between the 2 surgery groups; however, the fasting insulin concentrations were greater in the BND (10.0 microU/mL) than in the RYGB (6.2 microU/mL; P <0.05) group. The glucose level at 60 minutes was significantly lower in the RYGB group (70 mg/dL, range 38-82) than in the BND group (83 mg/dL, range 63-98). The GLP-1 levels at 30 minutes were more than threefold greater in the RYGB group (96 pmol/L) compared with the BND and overweight control (28 pmol/L) groups. The GLP-1 and insulin concentrations correlated at 30 minutes only in the RYGB group (r = .66; P = .013). The glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide levels at 30 minutes were lower in the RYGB group (20 pmol/L) than in the BND group (31 pmol/L) or overweight control group (33 pmol/L). The peak glucagon levels were similar among the 3 groups.
Conclusion: Exaggerated postprandial GLP-1 and blunted glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide secretion after RYGB might contribute to the greater weight loss and improved glucose homeostasis compared with BND.
Figures

References
-
- Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E, et al. Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2004;292:1724–37. - PubMed
-
- Cummings DE, Overduin J, Foster-Schubert KE. Gastric bypass for obesity: mechanisms of weight loss and diabetes resolution. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:2608–15. - PubMed
-
- Korner J, Inabnet W, Conwell IM, et al. Differential effects of gastric bypass and banding on circulating gut hormone and leptin levels. Obesity. 2006;14:1553–61. - PubMed
-
- Korner J, Bessler M, Cirilo LJ, et al. Effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery on fasting and postprandial concentrations of plasma ghrelin, peptide YY, and insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:359–65. - PubMed
-
- Drucker DJ. Minireview: the glucagon-like peptides. Endocrinology. 2001;142:521–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

