Cloning and expression profiling of testis-expressed microRNAs
- PMID: 17936267
- PMCID: PMC2121622
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.09.009
Cloning and expression profiling of testis-expressed microRNAs
Abstract
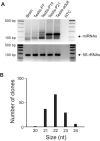
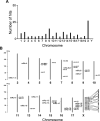
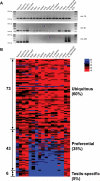
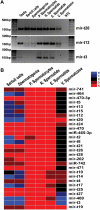
Using a new small RNA cloning method, we identified 141 miRNAs from the mouse testis, of which 29 were novel. The 141 miRNAs were mapped onto all chromosomes except the Y chromosome and 2/3 of these miRNA genes exist as clusters. approximately 70% of these miRNA genes were located in intronic or intergenic regions, whereas the remaining miRNAs were derived from exonic sequences. We further validated these cloned miRNAs by examining their expression in multiple mouse organs including developing testes and also in purified spermatogenic cells using semi-quantitative PCR analyses. Our expression profiling assays revealed that 60% of the testis-expressed miRNAs were ubiquitously expressed and the remaining are either preferentially (35%) or exclusively (5%) expressed in the testis. We also observed a lack of strand selection during testicular miRNA biogenesis, characterized by paired expression of both the 5' strands and 3' strands derived from the same precursor miRNAs. The present work identified numerous miRNAs preferentially or exclusively expressed in the testis, which would be interesting targets for further functional studies.
Figures
References
-
- Ambros V, Chen X. The regulation of genes and genomes by small RNAs. Development. 2007;134:1635–41. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97. - PubMed
-
- Bellve AR. Purification, culture, and fractionation of spermatogenic cells. Methods Enzymol. 1993;225:84–113. - PubMed
-
- Braun RE. Post-transcriptional control of gene expression during spermatogenesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 1998;9:483–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

