ASIC proteins regulate smooth muscle cell migration
- PMID: 17936312
- PMCID: PMC2293954
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mvr.2007.08.003
ASIC proteins regulate smooth muscle cell migration
Abstract
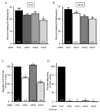
The purpose of the present study was to investigate Acid Sensing Ion Channel (ASIC) protein expression and importance in cellular migration. We recently demonstrated that Epithelial Na(+)Channel (ENaC) proteins are required for vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) migration; however, the role of the closely related ASIC proteins has not been addressed. We used RT-PCR and immunolabeling to determine expression of ASIC1, ASIC2, ASIC3 and ASIC4 in A10 cells. We used small interference RNA to silence individual ASIC expression and determine the importance of ASIC proteins in wound healing and chemotaxis (PDGF-bb)-initiated migration. We found ASIC1, ASIC2, and ASIC3, but not ASIC4, expression in A10 cells. ASIC1, ASIC2, and ASIC3 siRNA molecules significantly suppressed expression of their respective proteins compared to non-targeting siRNA (RISC) transfected controls by 63%, 44%, and 55%, respectively. Wound healing was inhibited by 10, 20, and 26% compared to RISC controls following suppression of ASIC1, ASIC2, and ASIC3, respectively. Chemotactic migration was inhibited by 30% and 45%, respectively, following suppression of ASIC1 and ASIC3. ASIC2 suppression produced a small, but significant, increase in chemotactic migration (4%). Our data indicate that ASIC expression is required for normal migration and may suggest a novel role for ASIC proteins in cellular migration.
Figures
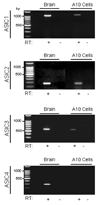

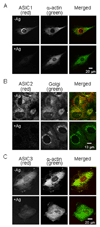
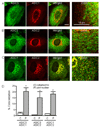
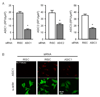

References
-
- Akopian AN, Chen CC, Ding Y, Cesare P, Wood JN. A new member of the acid-sensing ion channel family. Neuroreport. 2000;11:2217–2222. - PubMed
-
- Babinski K, Le KT, Seguela P. Molecular cloning and regional distribution of a human proton receptor subunit with biphasic functional properties. J Neurochem. 1999;72:51–57. - PubMed
-
- Bassilana F, Champigny G, Waldmann R, de Weille JR, Heurteaux C, Lazdunski M. The acid-sensitive ionic channel subunit ASIC and the mammalian degenerin MDEG form a heteromultimeric H+-gated Na+ channel with novel properties. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:28819–28822. - PubMed
-
- Berdiev BK, Xia J, McLean LA, Markert JM, Gillespie GY, Mapstone TB, Naren AP, Jovov B, Bubien JK, Ji HL, et al. Acid-sensing ion channels in malignant gliomas. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:15023–15034. - PubMed
-
- Bubien JK, Keeton DA, Fuller CM, Gillespie GY, Reddy AT, Mapstone TB, Benos DJ. Malignant human gliomas express an amiloride-sensitive Na+ conductance. Am J Physiol. 1999;276:C1405–C1410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

