Ctp1 is a cell-cycle-regulated protein that functions with Mre11 complex to control double-strand break repair by homologous recombination
- PMID: 17936710
- PMCID: PMC2066204
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.09.009
Ctp1 is a cell-cycle-regulated protein that functions with Mre11 complex to control double-strand break repair by homologous recombination
Abstract
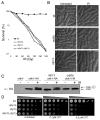
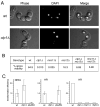
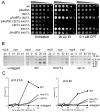
The Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 (MRN) complex is a primary sensor of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). Upon recruitment to DSBs, it plays a critical role in catalyzing 5' --> 3' single-strand resection that is required for repair by homologous recombination (HR). Unknown mechanisms repress HR in G1 phase of the cell cycle during which nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) is the favored mode of DSB repair. Here we describe fission yeast Ctp1, so-named because it shares conserved domains with the mammalian tumor suppressor CtIP. Ctp1 is recruited to DSBs where it is essential for repair by HR. Ctp1 is required for efficient formation of RPA-coated single-strand DNA adjacent to DSBs, indicating that it functions with the MRN complex in 5' --> 3' resection. Transcription of ctp1(+) is periodic during the cell cycle, with the onset of its expression coinciding with the start of DNA replication. These data suggest that regulation of Ctp1 underlies cell-cycle control of HR.
Figures
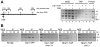


Comment in
-
Ctp1/CtIP and the MRN complex collaborate in the initial steps of homologous recombination.Mol Cell. 2007 Nov 9;28(3):351-2. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.10.016. Mol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17996697 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

