The Oct DNA motif participates in the alcohol inhibition of the inducible nitric oxide synthase gene promoter in rat C6 glioma cells
- PMID: 17936731
- PMCID: PMC2095129
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.08.047
The Oct DNA motif participates in the alcohol inhibition of the inducible nitric oxide synthase gene promoter in rat C6 glioma cells
Abstract
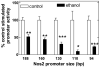
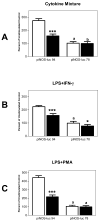
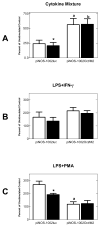
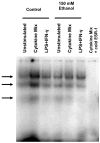
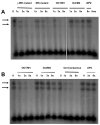
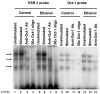
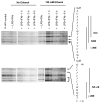
Induction of nitric oxide synthase-2 (iNOS) by cytokines and bacterial products is associated with protein binding at the proximal promoter and in an upstream enhancer region of the Nos2 gene. To clarify how ethanol suppresses rat iNOS activity, we constructed several deletion mutants of the Nos2 promoter fused to the luciferase gene and transfected the constructs into C6 glial cells. Acute ethanol exposure of stably transfected cells for 24 h inhibits induced activity of Nos2 promoter constructs containing deletions in the 5' flanking region, including a 94 bp promoter that lacks any known NF-kappaB site but which carries a C/EBPbeta and overlapping gamma-IRE, GAS and Oct motifs. Ethanol failed to inhibit the endogenous activity of a smaller, 78 bp promoter that lacks the C/EBPbeta and overlapping, gamma-IRE and GAS motifs and showed no inducible activity. As another approach, in vivo DNA footprinting was used and identified protein protections at five regions of the proximal Nos2 promoter in induced cells. Exposure to acute ethanol diminished protein occupation in the five promoter regions including the gamma-IRE/NF-kappaB and the overlapping gamma-IRE/GAS/Oct sites. Site-directed mutagenesis in the octamer domain of the gamma-IRE/GAS/Oct motifs was studied in a 1002 bp promoter to examine its role in ethanol inhibition of cytokine and lipopolysaccharide induced activity. The data indicate that ethanol failed to inhibit promoter activity when the Oct motif is missing. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays performed using a 22-mer probe containing the overlapping gamma-IRE/GAS/Oct sites showed three complexes with one of the complexes being competed by an octamer-1 antibody. These observations demonstrate the role of protein-DNA binding at the core promoter, and the likely involvement of the octamer motif, in ethanol modulation of cytokine and lipopolysaccharide induced iNOS expression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Octamer motif is required for the NF-kappaB-mediated induction of the inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages.Mol Cells. 1999 Feb 28;9(1):99-109. Mol Cells. 1999. PMID: 10102579
-
Cytokine-induced iNOS expression in C6 glial cells: transcriptional inhibition by ethanol.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001 Aug;298(2):744-52. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001. PMID: 11454939
-
Identification of cis-regulatory regions necessary for robust Nos2 promoter activity in glial cells: indirect role for NF-kappaB.J Neurochem. 2003 Sep;86(6):1379-90. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01943.x. J Neurochem. 2003. PMID: 12950447
-
alpha-MSH inhibits induction of C/EBPbeta-DNA binding activity and NOS2 gene transcription in macrophages.Kidney Int. 2000 Jun;57(6):2239-48. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.00084.x. Kidney Int. 2000. PMID: 10844594
-
In vivo footprinting of the mouse inducible nitric oxide synthase gene: inducible protein occupation of numerous sites including Oct and NF-IL6.Nucleic Acids Res. 1996 May 1;24(9):1682-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/24.9.1682. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996. PMID: 8649986 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A far-upstream Oct-1 motif regulates cytokine-induced transcription of the human inducible nitric oxide synthase gene.J Mol Biol. 2009 Jul 24;390(4):595-603. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.05.036. Epub 2009 May 23. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19467240 Free PMC article.
-
Adipose inflammation and macrophage infiltration after binge ethanol and burn injury.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014 Jan;38(1):204-13. doi: 10.1111/acer.12210. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014. PMID: 23909743 Free PMC article.
-
NOS Expression and NO Function in Glioma and Implications for Patient Therapies.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2017 Jun 10;26(17):986-999. doi: 10.1089/ars.2016.6820. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2017. PMID: 27411305 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adamson DC, Wildemann B, Sasaki M, Glass JD, McArthur JC, Christov VI, Dawson TM, Dawson VL. Immunologic NO synthase: elevation in severe AIDS dementia and induction by HIV-1 gp41. Science. 1996;274:1917–1921. - PubMed
-
- Belsham DD, Mellon PL. Transcription factors Oct-1 and C/EBPβ (CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-beta) are involved in the glutamate/nitric oxide/cyclic-guanosine 5′-monophosphate-mediated repression of mediated repression of gonadotropin-releasing hormone gene expression. Mol Endocrinol. 2000;14:212–228. - PubMed
-
- Bendall AJ, Sturm RA, Danoy PA, Molloy PL. Broad binding-site specificity and affinity properties of octamer 1 and brain octamer-binding proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1993;217:799–811. - PubMed
-
- Bhat NR, Feinstein DL, Shen Q, Bhat AN. p38 MAPK-mediated transcriptional activation of inducible nitric-oxide synthase in glial cells. Roles of nuclear factors, nuclear factor κB, cAMP response element-binding protein, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-β, and activating transcription factor-2. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:29584–29592. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

