Basic helix-loop-helix factors recruit nuclear factor I to enhance expression of the NaV 1.4 Na+ channel gene
- PMID: 17936922
- PMCID: PMC2176085
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbaexp.2007.08.004
Basic helix-loop-helix factors recruit nuclear factor I to enhance expression of the NaV 1.4 Na+ channel gene
Abstract
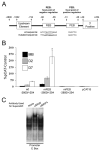
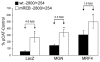
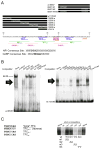
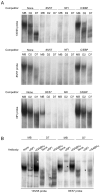
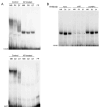
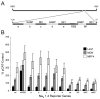
We have previously shown that the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors coordinate Na(V) 1.4 Na(+) channel gene expression in skeletal muscle, but the identity of the co-factors they direct is unknown. Using C2C12 muscle cells as a model system, we test the hypothesis that the bHLH factors counteract negative regulation exerted through a repressor E box (-90/-85) by recruiting positive-acting transcription factors to the nucleotides (-135/-57) surrounding the repressor E box. We used electrophoretic mobility shift assays to identify candidate factors that bound the repressor E box or these adjacent regions. Repressor E box-binding factors included the known transcription factor, ZEB/AREB6, and a novel repressor E box-binding factor designated REB. Mutations of the repressor E box that interfere with the binding of these factors prevented repression. The transcription factor, nuclear factor I (NFI), bound immediately upstream and downstream of the repressor E box. Mutation of the NFI-binding sites diminished the ability of myogenin and MRF4 to counteract repression. Based on these observations we suggest that bHLH factors recruit NFI to enhance skeletal muscle Na(+) channel expression.
Figures

References
-
- Kallen RG, Cohen SA, Barchi RL. Structure, function and expression of voltage-dependent sodium channels. Mol Neurobiol. 1993:383–428. - PubMed
-
- Rich MM, Pinter MJ, Kraner SD, Barchi RL. Loss of electrical excitability in an animal model of acute quadriplegic myopathy. Ann Neurol. 1998:171–9. - PubMed
-
- Rich MM, Kraner SD, Barchi RL. Altered gene expression in steroid-treated denervated muscle. Neurobiol Dis. 1999:515–22. - PubMed
-
- Waxman SG. Transcriptional channelopathies: an emerging class of disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001:652–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

