Discriminative motif discovery in DNA and protein sequences using the DEME algorithm
- PMID: 17937785
- PMCID: PMC2194741
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-385
Discriminative motif discovery in DNA and protein sequences using the DEME algorithm
Abstract
Background: Motif discovery aims to detect short, highly conserved patterns in a collection of unaligned DNA or protein sequences. Discriminative motif finding algorithms aim to increase the sensitivity and selectivity of motif discovery by utilizing a second set of sequences, and searching only for patterns that can differentiate the two sets of sequences. Potential applications of discriminative motif discovery include discovering transcription factor binding site motifs in ChIP-chip data and finding protein motifs involved in thermal stability using sets of orthologous proteins from thermophilic and mesophilic organisms.
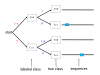
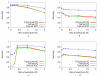
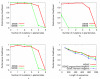
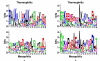
Results: We describe DEME, a discriminative motif discovery algorithm for use with protein and DNA sequences. Input to DEME is two sets of sequences; a "positive" set and a "negative" set. DEME represents motifs using a probabilistic model, and uses a novel combination of global and local search to find the motif that optimally discriminates between the two sets of sequences. DEME is unique among discriminative motif finders in that it uses an informative Bayesian prior on protein motif columns, allowing it to incorporate prior knowledge of residue characteristics. We also introduce four, synthetic, discriminative motif discovery problems that are designed for evaluating discriminative motif finders in various biologically motivated contexts. We test DEME using these synthetic problems and on two biological problems: finding yeast transcription factor binding motifs in ChIP-chip data, and finding motifs that discriminate between groups of thermophilic and mesophilic orthologous proteins.
Conclusion: Using artificial data, we show that DEME is more effective than a non-discriminative approach when there are "decoy" motifs or when a variant of the motif is present in the "negative" sequences. With real data, we show that DEME is as good, but not better than non-discriminative algorithms at discovering yeast transcription factor binding motifs. We also show that DEME can find highly informative thermal-stability protein motifs. Binaries for the stand-alone program DEME is free for academic use and is available at http://bioinformatics.org.au/deme/
Figures

References
-
- Tompa M, Li N, Bailey TL, Church GM, Moor BD, Eskin E, Favorov AV, Frith MC, Fu Y, Kent WJ, Makeev VJ, Mironov AA, Noble WS, Pavesi G, Pesole G, Régnier M, Simonis N, Sinha S, Thijs G, van Helden J, Vandenbogaert M, Weng Z, Workman C, Ye C, Zhu Z. Assessing computational tools for the discovery of transcription factor binding sites. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23:137–144. http://bioinformatics.org.au/deme/ - PubMed
-
- Liu XS, Brutlag DL, Liu JS. An algorithm for finding protein-DNA binding sites with applications to chromatin-immunoprecipitation microarray experiments. Nat Biotechnol. 2002;20:835–839. - PubMed
-
- Harbison CT, Gordon DB, Lee TI, Rinaldi NJ, Macisaac KD, Danford TW, Hannett NM, Tagne JB, Reynolds DB, Yoo J, Jennings EG, Zeitlinger J, Pokholok DK, Kellis M, Rolfe PA, Takusagawa KT, Lander ES, Gifford DK, Fraenkel E, Young RA. Transcriptional regulatory code of a eukaryotic genome. Nature. 2004;431:99–104. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

