Early pancreatic development requires the vertebrate Suppressor of Hairless (RBPJ) in the PTF1 bHLH complex
- PMID: 17938243
- PMCID: PMC2000326
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1575207
Early pancreatic development requires the vertebrate Suppressor of Hairless (RBPJ) in the PTF1 bHLH complex
Abstract
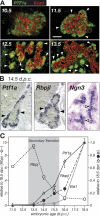
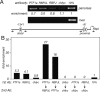
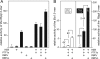
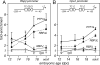
PTF1a is an unusual basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor that is required for the development of the pancreas. We show that early in pancreatic development, active PTF1a requires interaction with RBPJ, the vertebrate Suppressor of Hairless, within a stable trimeric DNA-binding complex (PTF1). Later, as acinar cell development begins, RBPJ is swapped for RBPJL, the constitutively active, pancreas-restricted paralog of RBPJ. Moreover, the Rbpjl gene is a direct target of the PTF1 complex: At the onset of acinar cell development when the Rbpjl gene is first induced, a PTF1 complex containing RBPJ is bound to the Rbpjl promoter. As development proceeds, RBPJL gradually replaces RBPJ in the PTF1 complex bound to Rbpjl and appears on the binding sites for the complex in the promoters of other acinar-specific genes, including those for the secretory digestive enzymes. A single amino acid change in PTF1a that eliminates its ability to bind RBPJ (but does not affect its binding to RBPJL) causes pancreatic development to truncate at an immature stage, without the formation of acini or islets. These results indicate that the interaction between PTF1a and RBPJ is required for the early stage of pancreatic growth, morphogenesis, and lineage fate decisions. The defects in pancreatic development phenocopy those of Ptf1a-null embryos; thus, the first critical function of PTF1a is in the context of the PTF1 complex containing RBPJ. Action within an organ-specific transcription factor is a previously unknown function for RBPJ and is independent of its role in Notch signaling.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Replacement of Rbpj with Rbpjl in the PTF1 complex controls the final maturation of pancreatic acinar cells.Gastroenterology. 2010 Jul;139(1):270-80. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.04.003. Epub 2010 Apr 14. Gastroenterology. 2010. PMID: 20398665 Free PMC article.
-
PTF1 is an organ-specific and Notch-independent basic helix-loop-helix complex containing the mammalian Suppressor of Hairless (RBP-J) or its paralogue, RBP-L.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Jan;26(1):117-30. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.1.117-130.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16354684 Free PMC article.
-
Neurog2 is a direct downstream target of the Ptf1a-Rbpj transcription complex in dorsal spinal cord.Development. 2009 Sep;136(17):2945-54. doi: 10.1242/dev.035352. Epub 2009 Jul 29. Development. 2009. PMID: 19641016 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor Ptf1a in development, diseases and reprogramming.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Mar;76(5):921-940. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2972-z. Epub 2018 Nov 23. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30470852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Notch-independent functions of CSL.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2011;97:55-74. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385975-4.00009-7. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 22074602 Review.
Cited by
-
Endocrine pancreatic development: impact of obesity and diet.Front Physiol. 2013 Jul 18;4:170. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00170. eCollection 2013. Front Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23882220 Free PMC article.
-
Jagged 1 is necessary for normal mouse lens formation.Dev Biol. 2009 Apr 1;328(1):118-26. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.01.015. Epub 2009 Jan 20. Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19389370 Free PMC article.
-
Pias3-dependent SUMOylation directs rod photoreceptor development.Neuron. 2009 Jan 29;61(2):234-46. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.12.006. Neuron. 2009. PMID: 19186166 Free PMC article.
-
Replacement of Rbpj with Rbpjl in the PTF1 complex controls the final maturation of pancreatic acinar cells.Gastroenterology. 2010 Jul;139(1):270-80. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.04.003. Epub 2010 Apr 14. Gastroenterology. 2010. PMID: 20398665 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular signaling in pancreatic ductal metaplasia: emerging biomarkers for detection and intervention of early pancreatic cancer.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2022 Apr;45(2):201-225. doi: 10.1007/s13402-022-00664-x. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2022. PMID: 35290607 Review.
References
-
- Ahlgren U., Jonsson J., Edlund H., Jonsson J., Edlund H., Edlund H. The morphogenesis of the pancreatic mesenchyme is uncoupled from that of the pancreatic epithelium in IPF1/PDX1-deficient mice. Development. 1996;122:1409–1416. - PubMed
-
- Apelqvist A., Li H., Sommer L., Beatus P., Anderson D.J., Honjo T., de Hrabe Angelis M., Lendahl U., Edlund H., Li H., Sommer L., Beatus P., Anderson D.J., Honjo T., de Hrabe Angelis M., Lendahl U., Edlund H., Sommer L., Beatus P., Anderson D.J., Honjo T., de Hrabe Angelis M., Lendahl U., Edlund H., Beatus P., Anderson D.J., Honjo T., de Hrabe Angelis M., Lendahl U., Edlund H., Anderson D.J., Honjo T., de Hrabe Angelis M., Lendahl U., Edlund H., Honjo T., de Hrabe Angelis M., Lendahl U., Edlund H., de Hrabe Angelis M., Lendahl U., Edlund H., Lendahl U., Edlund H., Edlund H. Notch signalling controls pancreatic cell differentiation. Nature. 1999;400:877–881. - PubMed
-
- Beres T.M., Masui T., Swift G.H., Shi L., Henke R.M., MacDonald R.J., Masui T., Swift G.H., Shi L., Henke R.M., MacDonald R.J., Swift G.H., Shi L., Henke R.M., MacDonald R.J., Shi L., Henke R.M., MacDonald R.J., Henke R.M., MacDonald R.J., MacDonald R.J. PTF1 is an organ-specific and Notch-independent basic helix–loop–helix complex containing the mammalian Suppressor of Hairless (RBP-J) or its paralogue, RBP-L. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006;26:117–130. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Birren S.J., Lo L., Anderson D.J., Lo L., Anderson D.J., Anderson D.J. Sympathetic neuroblasts undergo a developmental switch in trophic dependence. Development. 1993;119:597–610. - PubMed
-
- Brinster R.L., Chen H.Y., Trumbauer M.E., Yagle M.K., Palmiter R.D., Chen H.Y., Trumbauer M.E., Yagle M.K., Palmiter R.D., Trumbauer M.E., Yagle M.K., Palmiter R.D., Yagle M.K., Palmiter R.D., Palmiter R.D. Factors affecting the efficiency of introducing foreign DNA into mice by microinjecting eggs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1985;82:4438–4442. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
