Analysis of electroblotted proteins by mass spectrometry: protein identification after Western blotting
- PMID: 17938404
- PMCID: PMC2667373
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M700415-MCP200
Analysis of electroblotted proteins by mass spectrometry: protein identification after Western blotting
Abstract
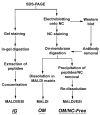
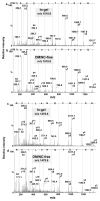
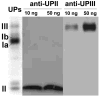
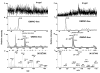
We describe a new approach for the identification and characterization by mass spectrometry of proteins that have been electroblotted onto nitrocellulose. Using this method (Blotting and Removal of Nitrocellulose (BARN)), proteins can be analyzed either as intact proteins for molecular weight determination or as peptides generated by on-membrane proteolysis. Acetone is used to dissolve the nitrocellulose and to precipitate the adsorbed proteins/peptides, thus removing the nitrocellulose which can interfere with MS analysis. This method offers improved protein coverage, especially for membrane proteins, such as uroplakins, because the extraction step after in-gel digestion is avoided. Moreover, removal of nitrocellulose from the sample solution allows sample analysis by both MALDI- and (LC) ESI-based mass spectrometers. Finally, we demonstrate the utility of BARN for the direct identification of soluble and membrane proteins after Western blotting, obtaining comparable or better results than with in-gel digestion.
Figures

Similar articles
-
On-membrane tryptic digestion of proteins for mass spectrometry analysis.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;536:331-41. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-542-8_35. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19378072 Free PMC article.
-
Use of nitrocellulose membranes for protein characterization by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry.Anal Chem. 2006 Jul 15;78(14):5102-8. doi: 10.1021/ac060344t. Anal Chem. 2006. PMID: 16841935 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Electroblotted Proteins by Mass Spectrometry.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1314:243-53. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2718-0_25. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26139272 Free PMC article.
-
A brief review of other notable protein blotting methods.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;536:367-84. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-542-8_38. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19378075 Review.
-
Methods in enzymology: O-glycosylation of proteins.Methods Enzymol. 2005;405:139-71. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)05007-X. Methods Enzymol. 2005. PMID: 16413314 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Ablation of MiR-22 Fosters Diet-Induced Obesity and NAFLD Development.J Pers Med. 2020 Oct 14;10(4):170. doi: 10.3390/jpm10040170. J Pers Med. 2020. PMID: 33066497 Free PMC article.
-
A simple and rapid pipeline for identification of receptor-binding sites on the surface proteins of pathogens.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 24;10(1):1163. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58305-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31980725 Free PMC article.
-
On-membrane tryptic digestion of proteins for mass spectrometry analysis.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;536:331-41. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-542-8_35. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19378072 Free PMC article.
-
Two-dimensional southwestern blotting and characterization of transcription factors on-blot.J Proteome Res. 2009 Jul;8(7):3693-701. doi: 10.1021/pr900214p. J Proteome Res. 2009. PMID: 19388704 Free PMC article.
-
Functional amyloids in the mouse sperm acrosome.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Jul;34(14):2624-34. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00073-14. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24797071 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shevchenko A, Wilm M, Vorm O, Mann M. Mass spectrometric sequencing of proteins silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. Anal Chem. 1996;68:850–858. - PubMed
-
- Jonsson AP, Aissouni Y, Palmberg C, Percipalle P, Nordling E, Daneholt B, Jornvall H, Bergman T. Recovery of gel-separated proteins for in-solution digestion and mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2001;73:5370–5377. - PubMed
-
- van Oostveen I, Ducret A, Aebersold R. Colloidal silver staining of electroblotted proteins for high sensitivity peptide mapping by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem. 1997;247:310–318. - PubMed
-
- Liang X, Bai J, Liu YH, Lubman DM. Characterization of SDS--PAGE-separated proteins by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 1996;68:1012–1018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

