Preoperative laxity in osteoarthritis patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty
- PMID: 17938923
- PMCID: PMC2899222
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-007-0467-x
Preoperative laxity in osteoarthritis patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty
Abstract
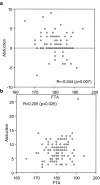
A preoperative quantitative evaluation of soft tissues is helpful for planning total knee arthroplasty, in addition to the conventional clinical examinations involved in moving the knee manually. We evaluated preoperative coronal laxity with osteoarthritis in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty by applying a force of 150 N with an arthrometer. We examined a consecutive series of 120 knees in 102 patients. The median laxity was 0 degrees in abduction and 8 degrees in adduction. The femorotibial angle on non-weight-bearing standard anteroposterior radiographs was 180 degrees and correlated with both abduction (r = -0.244, p = 0.007) and adduction (r = 0.205, p = 0.025) laxity. The results of a regression analysis suggested that the femorotibial angle is helpful for estimating both laxities. Considering the many reports on how to obtain well-balanced soft tissues, stress radiographs might help to improve the preoperative planning for gaining the optimal laxity deemed appropriate by surgeons.
Une analyse avec évaluation quantitative préopératoire des tissus mous est nécessaire dans la planification d’une prothèse totale de genou, ceci en plus des examens cliniques conventionnels, notamment en ce qui concerne l’évaluation de la mobilité. Nous avons évalué, en préopératoire, les laxités ainsi que les stades de l’arthrose chez les patients qui ont bénéficié d’une prothèse totale du genou. Ces résultats ont été réalisés à l’arthromètre. Nous avons réalisé une série consécutive de 120 genoux chez 102 patients. La laxité moyenne était de 0° en abduction et de 8° en adduction. L’angle fémoro tibial, sans appui, sur les radiographies de face et de profil était de 180° et a été corrélé avec la laxité en abduction (r = −0.244, p = 0.007) et en adduction (r = 0.205, p = 0.025). Les résultats nous montrent que l’angle fémoro tibial est utile pour estimer les laxités. Si l’on considère les différentes études et la meilleure manière d’obtenir une bonne balance ligamentaire, les radiographies en stress permettent d’optimiser le planning opératoire et d’avoir une bonne idée des laxités.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Medial and lateral laxity in knees with advanced medial osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018 May;26(5):666-670. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2018.01.027. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018. PMID: 29428318
-
Mediolateral coronal laxity does not correlate with knee range of motion after total knee arthroplasty.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019 Jun;139(6):851-858. doi: 10.1007/s00402-019-03161-3. Epub 2019 Mar 11. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019. PMID: 30859302
-
The effect of anteroposterior laxity on the range of movement and knee function following a cruciate-retaining total knee replacement.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010 Aug;92(8):1090-5. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.92B8.23980. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010. PMID: 20675752
-
The Varus Osteoarthritic Knee Has No Coronal Contractures in 90 Degrees of Flexion.J Knee Surg. 2017 May;30(4):297-303. doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1584539. Epub 2016 Jul 1. J Knee Surg. 2017. PMID: 27367204
-
High prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in elderly patients with advanced osteoarthritis scheduled for total knee replacement associated with poorer preoperative functional state.Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2013 Nov;95(8):569-72. doi: 10.1308/rcsann.2013.95.8.569. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2013. PMID: 24165338 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Patient specific variables impact sensitivity to association between joint balance and 2 Year outcomes.J Orthop. 2024 Dec 12;65:71-77. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2024.12.007. eCollection 2025 Jul. J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39801901
-
The difference between weight-bearing and non-weight-bearing alignment in patient-specific instrumentation planning.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014 Mar;22(3):674-9. doi: 10.1007/s00167-013-2687-5. Epub 2013 Sep 20. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014. PMID: 24051507
-
Second-generation bi-cruciate stabilized total knee system has a lower reoperation and revision rate than its predecessor.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018 Nov;138(11):1591-1599. doi: 10.1007/s00402-018-3019-5. Epub 2018 Aug 25. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018. PMID: 30167859 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-operative frontal plane malalignment predicts the extension gap asymmetry in knee osteoarthritis.Int Orthop. 2012 Jan;36(1):79-82. doi: 10.1007/s00264-011-1294-7. Epub 2011 Jun 15. Int Orthop. 2012. PMID: 21674289 Free PMC article.
-
Lateral soft tissue laxity increases but medial laxity does not contract with varus deformity in total knee arthroplasty.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013 Apr;471(4):1334-42. doi: 10.1007/s11999-012-2745-1. Epub 2012 Dec 18. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013. PMID: 23247818 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buckland-Wright JC, Wolfe F, Ward RJ, Flowers N, Hayne C. Substantial superiority of semiflexed (MTP) views in knee osteoarthritis: a comparative radiographic study, without fluoroscopy, of standing extended, semiflexed (MTP), and Schuss views. J Rheumatol. 1999;26:2664–2674. - PubMed
-
- Conrozier T, Favret H, Mathieu P, Piperno M, Provvedini D, Taccoen A, Colson F, Conrozier S, Vignon E. Influence of the quality of tibial plateau alignment on the reproducibility of computer joint space measurement from Lyon Schuss radiographic views of the knee in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarth Cartil. 2004;12:765–770. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2004.06.003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

