Cyclic changes in metabolic state during the life of a yeast cell
- PMID: 17940006
- PMCID: PMC2040445
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0708365104
Cyclic changes in metabolic state during the life of a yeast cell
Abstract
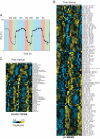
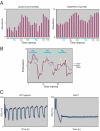
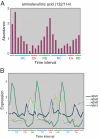
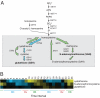
Budding yeast undergo robust oscillations in oxygen consumption during continuous growth in a nutrient-limited environment. Using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and comprehensive 2D gas chromatography-mass spectrometry-based metabolite profiling methods, we have determined that the intracellular concentrations of many metabolites change periodically as a function of these metabolic cycles. These results reveal the logic of cellular metabolism during different phases of the life of a yeast cell. They may further indicate that oscillation in the abundance of key metabolites might help control the temporal regulation of cellular processes and the establishment of a cycle. Such oscillations in metabolic state might occur during the course of other biological cycles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wijnen H, Young MW. Annu Rev Genet. 2006;40:409–448. - PubMed
-
- Harmer SL, Hogenesch JB, Straume M, Chang HS, Han B, Zhu T, Wang X, Kreps JA, Kay SA. Science. 2000;290:2110–2113. - PubMed
-
- Claridge-Chang A, Wijnen H, Naef F, Boothroyd C, Rajewsky N, Young MW. Neuron. 2001;32:657–671. - PubMed
-
- McDonald MJ, Rosbash M. Cell. 2001;107:567–578. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

