Therapeutic silencing of mutant huntingtin with siRNA attenuates striatal and cortical neuropathology and behavioral deficits
- PMID: 17940007
- PMCID: PMC2040405
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0708285104
Therapeutic silencing of mutant huntingtin with siRNA attenuates striatal and cortical neuropathology and behavioral deficits
Abstract
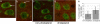
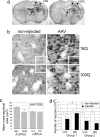
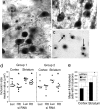
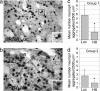
Huntington's disease (HD) is a neurodegenerative disorder caused by expansion of a CAG repeat in the huntingtin (Htt) gene. HD is autosomal dominant and, in theory, amenable to therapeutic RNA silencing. We introduced cholesterol-conjugated small interfering RNA duplexes (cc-siRNA) targeting human Htt mRNA (siRNA-Htt) into mouse striata that also received adeno-associated virus containing either expanded (100 CAG) or wild-type (18 CAG) Htt cDNA encoding huntingtin (Htt) 1-400. Adeno-associated virus delivery to striatum and overlying cortex of the mutant Htt gene, but not the wild type, produced neuropathology and motor deficits. Treatment with cc-siRNA-Htt in mice with mutant Htt prolonged survival of striatal neurons, reduced neuropil aggregates, diminished inclusion size, and lowered the frequency of clasping and footslips on balance beam. cc-siRNA-Htt was designed to target human wild-type and mutant Htt and decreased levels of both in the striatum. Our findings indicate that a single administration into the adult striatum of an siRNA targeting Htt can silence mutant Htt, attenuate neuronal pathology, and delay the abnormal behavioral phenotype observed in a rapid-onset, viral transgenic mouse model of HD.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: P.D.Z. is a cofounder and scientific advisory board member of Alnylam Pharmaceuticals. D.W.Y.S., M.M., K.G.R., and R.K.P. are employees of Alnylam Pharmaceuticals.
Figures

References
-
- Huntington's Disease Collaborative Research Group. Cell. 1993;72:971–983. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto A, Lucas JJ, Hen R. Cell. 2000;101:57–66. - PubMed
-
- Singer O, Marr RA, Rockenstein E, Crews L, Coufal NG, Gage FH, Verma IM, Masliah E. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:1343–1349. - PubMed
-
- Raoul C, Abbas-Terki T, Bensadoun JC, Guillot S, Haase G, Szulc J, Henderson CE, Aebischer P. Nat Med. 2005;11:423–428. - PubMed
-
- Xia H, Mao Q, Eliason SL, Harper SQ, Martins IH, Orr HT, Paulson HL, Yang L, Kotin RM, Davidson BL. Nat Med. 2004;10:816–820. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

