S-nitrosohemoglobin deficiency: a mechanism for loss of physiological activity in banked blood
- PMID: 17940022
- PMCID: PMC2040473
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0707958104
S-nitrosohemoglobin deficiency: a mechanism for loss of physiological activity in banked blood
Abstract
RBCs distribute oxygen to tissues, but, paradoxically, blood transfusion does not always improve oxygen delivery and is associated with ischemic events. We hypothesized that storage of blood would result in loss of NO bioactivity, impairing RBC vasodilation and thus compromising blood flow, and that repleting NO bioactivity would restore RBC function. We report that S-nitrosohemoglobin (SNO-Hb) concentrations declined rapidly after storage of fresh venous blood and that hypoxic vasodilation by banked RBCs correlated strongly with the amounts of SNO-Hb (r(2) = 0.90; P < 0.0005). Renitrosylation of banked blood during storage increased the SNO-Hb content and restored its vasodilatory activity. In addition, canine coronary blood flow was greater during infusion of renitrosylated RBCs than during infusion of S-nitrosothiol-depleted RBCs, and this difference in coronary flow was accentuated by hypoxemia (P < 0.001). Our findings indicate that NO bioactivity is depleted in banked blood, impairing the vasodilatory response to hypoxia, and they suggest that SNO-Hb repletion may improve transfusion efficacy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: J.S.S. and J.D.R. have consulting and/or equity relationships with Nitrox/N30, a company that is developing strategies for treating disorders of oxygen delivery
Figures

 , P < 0.05 (significant difference from fresh blood). At day 21, the level of SNO-Hb was below the sensitivity of the assay (ND, not detected).
, P < 0.05 (significant difference from fresh blood). At day 21, the level of SNO-Hb was below the sensitivity of the assay (ND, not detected).
 are time points where SNO-Hb levels were significantly reduced compared with fresh blood (P < 0.05). Similarly, vasorelaxations marked with
are time points where SNO-Hb levels were significantly reduced compared with fresh blood (P < 0.05). Similarly, vasorelaxations marked with  were significantly less (P < 0.01) than those produced by fresh RBCs. Each time point is an independent sampling comprising different individuals. (B) Cohort B: Change in SNO-Hb concentration over time from serially sampled blood bags obtained at day 2 (n = 6); SNO-Hb is significantly reduced at all time points compared with fresh venous blood. Blood in cohorts A and B was obtained from the same commercial source.
were significantly less (P < 0.01) than those produced by fresh RBCs. Each time point is an independent sampling comprising different individuals. (B) Cohort B: Change in SNO-Hb concentration over time from serially sampled blood bags obtained at day 2 (n = 6); SNO-Hb is significantly reduced at all time points compared with fresh venous blood. Blood in cohorts A and B was obtained from the same commercial source.
 , time points where SNO-Hb and HbNO levels in untreated blood were significantly reduced compared with fresh blood (P < 0.05); †, the time point (day 43) where SNO-Hb and total NO levels in treated blood remained significantly reduced compared with fresh blood (P < 0.05).
, time points where SNO-Hb and HbNO levels in untreated blood were significantly reduced compared with fresh blood (P < 0.05); †, the time point (day 43) where SNO-Hb and total NO levels in treated blood remained significantly reduced compared with fresh blood (P < 0.05).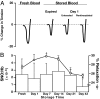
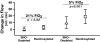
Comment in
-
Clinical implications of the loss of vasoactive nitric oxide during red blood cell storage.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Dec 4;104(49):19165-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0708871105. Epub 2007 Nov 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 18048331 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Optimized S-nitrosohemoglobin Synthesis in Red Blood Cells to Preserve Hypoxic Vasodilation Via βCys93.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2022 Jul;382(1):1-10. doi: 10.1124/jpet.122.001194. Epub 2022 May 5. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2022. PMID: 35512801 Free PMC article.
-
Renitrosylation of banked human red blood cells improves deformability and reduces adhesivity.Transfusion. 2015 Oct;55(10):2452-63. doi: 10.1111/trf.13189. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Transfusion. 2015. PMID: 26098062 Free PMC article.
-
SNO-hemoglobin is not essential for red blood cell-dependent hypoxic vasodilation.Nat Med. 2008 Jul;14(7):773-7. doi: 10.1038/nm1771. Epub 2008 May 30. Nat Med. 2008. PMID: 18516054 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Nitric Oxide Carried by Hemoglobin in Cardiovascular Physiology: Developments on a Three-Gas Respiratory Cycle.Circ Res. 2020 Jan 3;126(1):129-158. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.315626. Epub 2019 Oct 8. Circ Res. 2020. PMID: 31590598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Red Blood Cell-Mediated S-Nitrosohemoglobin-Dependent Vasodilation: Lessons Learned from a β-Globin Cys93 Knock-In Mouse.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2021 Apr 20;34(12):936-961. doi: 10.1089/ars.2020.8153. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2021. PMID: 32597195 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anemia in critical illness: insights into etiology, consequences, and management.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012 May 15;185(10):1049-57. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201110-1915CI. Epub 2012 Jan 26. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012. PMID: 22281832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FEEding DURing red cell transfusion (FEEDUR RCT): a multi-arm randomised controlled trial.BMC Pediatr. 2020 Jul 14;20(1):346. doi: 10.1186/s12887-020-02233-3. BMC Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32664953 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Red Blood Cell Dysfunction in Critical Illness.Crit Care Clin. 2020 Apr;36(2):267-292. doi: 10.1016/j.ccc.2019.12.008. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Crit Care Clin. 2020. PMID: 32172813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transfusion related morbidity in premature babies: Possible mechanisms and implications for practice.World J Clin Pediatr. 2014 Aug 8;3(3):19-29. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v3.i3.19. eCollection 2014 Aug 8. World J Clin Pediatr. 2014. PMID: 25254181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Hematocrit and Red Blood Cell Transfusion with Outcomes in Infants Undergoing Norwood Operation.Pediatr Cardiol. 2015 Aug;36(6):1212-8. doi: 10.1007/s00246-015-1147-z. Epub 2015 Mar 15. Pediatr Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25773580
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

