Relationship of fat distribution with adipokines in human immunodeficiency virus infection
- PMID: 17940113
- PMCID: PMC2190751
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2007-1155
Relationship of fat distribution with adipokines in human immunodeficiency virus infection
Abstract
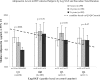
Background and methods: HIV-infected patients receiving antiretroviral therapy often develop changes in body fat distribution; the dominant change is reduction in sc adipose tissue (SAT). Because adipose tissue makes important hormones involved in whole-body energy metabolism, including leptin and adiponectin, we examined plasma concentrations and their relationship to regional adiposity measured by magnetic resonance imaging in 1143 HIV-infected persons (803 men and 340 women) and 286 controls (151 men and 135 women) in a cross-sectional analysis of the FRAM study.
Results: Total and regional adiposity correlated positively with leptin levels in HIV-infected subjects and controls (P < 0.0001). In controls, total and regional adiposity correlated negatively with adiponectin. In HIV-infected subjects, adiponectin was not significantly correlated with total adiposity, but the normal negative correlation with visceral adipose tissue and upper trunk SAT was maintained. However, leg SAT was positively associated with adiponectin in HIV-infected subjects. Within the lower decile of leg SAT for controls, HIV-infected subjects had paradoxically lower adiponectin concentrations compared with controls (men: HIV 4.1 microg/ml vs. control 7.5 microg/ml, P = 0.009; women: HIV 7.8 microg/ml vs. control 11.6 microg/ml, P = 0.037). Even after controlling for leg SAT, exposure to stavudine was associated with lower adiponectin, predominantly in those with lipoatrophy.
Conclusion: The normal relationships between adiponectin levels and total and leg adiposity are lost in HIV-infected subjects, possibly due to changes in adipocyte function associated with HIV lipodystrophy, whereas the inverse association of adiponectin and visceral adipose tissue is maintained. In contrast, the relationship between adiposity and leptin levels appears similar to controls and unaffected by HIV lipodystrophy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adipocyte-derived hormone levels in HIV lipodystrophy.Antivir Ther. 2003 Feb;8(1):9-15. Antivir Ther. 2003. PMID: 12713059
-
Regional adipose tissue measured by MRI over 5 years in HIV-infected and control participants indicates persistence of HIV-associated lipoatrophy.AIDS. 2010 Jul 17;24(11):1717-26. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32833ac7a2. AIDS. 2010. PMID: 20502316 Free PMC article.
-
Regional fat deposition and cardiovascular risk in HIV infection: the FRAM study.AIDS Care. 2011 Aug;23(8):929-38. doi: 10.1080/09540121.2010.543885. Epub 2011 Jun 24. AIDS Care. 2011. PMID: 21767228 Free PMC article.
-
Visceral adiposity and inflammatory bowel disease.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021 Nov;36(11):2305-2319. doi: 10.1007/s00384-021-03968-w. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021. PMID: 34104989 Review.
-
Immunological functions of leptin and adiponectin.Biochimie. 2012 Oct;94(10):2082-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2012.05.018. Epub 2012 Jun 26. Biochimie. 2012. PMID: 22750129 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and magnetic resonance imaging-measured adipose tissue depots in HIV-infected and control subjects.Am J Clin Nutr. 2008 Oct;88(4):1088-96. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/88.4.1088. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008. PMID: 18842798 Free PMC article.
-
C1q/TNF-Related Proteins, HIV and HIV-Associated Factors, and Cardiometabolic Phenotypes in Middle-Aged Women.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2019 Nov/Dec;35(11-12):1054-1064. doi: 10.1089/AID.2019.0099. Epub 2019 Sep 3. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2019. PMID: 31359766 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Dysregulation in Myocardial Fibrosis, Steatosis, and Heart Failure: Current Insights from HIV and the General Population.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2021 Feb;18(1):63-72. doi: 10.1007/s11904-020-00536-9. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2021. PMID: 33433816 Review.
-
Comparison of body composition changes between atazanavir/ritonavir and lopinavir/ritonavir each in combination with tenofovir/emtricitabine in antiretroviral-naïve patients with HIV-1 infection.Clin Drug Investig. 2014 Apr;34(4):287-96. doi: 10.1007/s40261-014-0175-4. Clin Drug Investig. 2014. PMID: 24557728 Clinical Trial.
-
Association of increased upper trunk and decreased leg fat with 2-h glucose in control and HIV-infected persons.Diabetes Care. 2011 Nov;34(11):2448-53. doi: 10.2337/dc11-0616. Epub 2011 Sep 16. Diabetes Care. 2011. PMID: 21926283 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kershaw EE, Flier JS 2004 Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:2548–2556 - PubMed
-
- Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, Kriauciunas A, Stephens TW, Nyce MR, Ohannesian JP, Marco CC, McKee LJ, Bauer T, Caro JF 1996 Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N Engl J Med 334:292–295 - PubMed
-
- Grinspoon S, Gulick T, Askari H, Landt M, Lee K, Anderson E, Ma Z, Vignati L, Bowsher R, Herzog D, Klibanski A 1996 Serum leptin levels in women with anorexia nervosa. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:3861–3863 - PubMed
-
- Haque WA, Shimomura I, Matsuzawa Y, Garg A 2002 Serum adiponectin and leptin levels in patients with lipodystrophies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:2395–2398 - PubMed
-
- Wong SP, Huda M, English P, Bargiotta A, Wilding JP, Johnson A, Corrall R, Pinkney JH 2005 Adipokines and the insulin resistance syndrome in familial partial lipodystrophy caused by a mutation in lamin A/C. Diabetologia 48:2641–2649 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RR00865/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK040990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RR00051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000054/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000052/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR00052/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL074814/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RR0636/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000083/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR00054/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK57508/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK057508/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RR00083/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HL 74814/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000865/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000036/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HL 53359/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00036/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

