Progestin-inflammatory cytokine interactions affect matrix metalloproteinase-1 and -3 expression in term decidual cells: implications for treatment of chorioamnionitis-induced preterm delivery
- PMID: 17940116
- PMCID: PMC2190749
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2007-1538
Progestin-inflammatory cytokine interactions affect matrix metalloproteinase-1 and -3 expression in term decidual cells: implications for treatment of chorioamnionitis-induced preterm delivery
Abstract
Context: Chorioamnionitis (CAM)-elicited preterm delivery (PTD) is associated with elevated amniotic fluid levels of IL-1beta and TNF-alpha. We hypothesized that IL-1beta and TNF-alpha may induce matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-1 and MMP-3 activity to promote PTD by degrading decidual and fetal membranes and cervical extracellular matrix.
Objective: Our objective was to evaluate: 1) MMP-1 and MMP-3 expression in decidual sections from uncomplicated term, idiopathic preterm, and CAM-complicated deliveries, and 2) the separate and interactive effects of IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA), and a p38 MAPK inhibitor (SB203580) on MMP-1 and MMP-3 expression in term decidual cells (DCs).
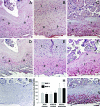
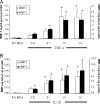
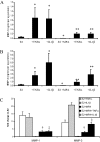
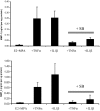
Interventions and main outcome measures: Decidua were immunostained for MMP-1 and MMP-3. Cultured term DCs were incubated with estradiol (E2) or E2 plus MPA with or without IL-1beta or TNF-alpha with or without SB203580. ELISA and Western blotting assessed secreted MMP-1 and MMP-3 levels, quantitative real-time RT-PCR assessed mRNA levels, and substrate gel zymography was used to determined MMP-1 and MMP-3 proteolytic activity.
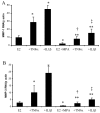
Results: MMP-1 and MMP-3 immunostaining was more prominent in CAM-complicated decidua vs. control preterm and term decidual specimens (P < 0.05). Compared with basal outputs by DCs incubated with E2, TNF-alpha enhanced MMP-1 and MMP-3 secretion by 14 +/- 3- and 9 +/- 2-fold, respectively, and IL-1beta increased MMP-1 and MMP-3 secretion by 13 +/- 3- and 19 +/- 2-fold, respectively (P < 0.05). Addition of MPA lowered basal MMP-1 and MMP-3 outputs by 70%, whereas the TNF-alpha- and IL-1beta-enhanced MMP-1 and MMP-3 levels were blunted by more than 50% (P < 0.05). SB203580 suppressed TNF-alpha- and IL-1beta-induced MMP-1 and MMP-3 secretion by severalfold. Western blotting confirmed the ELISA results, and mRNA levels corresponded with MMP-1 and MMP-3 protein levels. MMP-1 and MMP-3 proteolytic activity was confirmed by substrate gel zymography.
Conclusion: Augmented DC-expressed MMP-1 and MMP-3 in CAM-complicated pregnancies may promote PTD via decidual, fetal membrane, and cervical extracellular matrix degradation. Effects of progestin-p38 MAPK signaling inhibition on cytokine-enhanced MMP-1 and MMP-3 expression in term DCs suggest alternative mechanisms to prevent CAM-induced PTD.
Figures

References
-
- Mueller-Heubach E, Rubinstein DN, Schwarz SS 1990 Histologic chorioamnionitis and preterm delivery in different patient populations. Obstet Gynecol 75:622–626 - PubMed
-
- Lockwood CJ, Kuczynski E 1999 Markers of risk for preterm delivery. J Perinat Med 27:5–20 - PubMed
-
- Hamilton BE, Martin JA, Ventura SJ 2006 Births: preliminary data for 2005. Natl Vital Stat Rep 55:1–18 - PubMed
-
- Newton ER 2005 Preterm labor, preterm premature rupture of membranes, and chorioamnionitis. Clin Perinatol 32:571–600 - PubMed
-
- Shim SS, Romero R, Hong JS, Park CW, Jun JK, Kim BI, Yoon BH 2004 Clinical significance of intra-amniotic inflammation in patients with preterm premature rupture of membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol 191:1339–1345 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

