Experimental test of scaling of mixing by chaotic advection in droplets moving through microfluidic channels
- PMID: 17940580
- PMCID: PMC2025702
- DOI: 10.1063/1.1630378
Experimental test of scaling of mixing by chaotic advection in droplets moving through microfluidic channels
Abstract
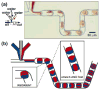
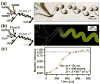
This letter describes an experimental test of a simple argument that predicts the scaling of chaotic mixing in a droplet moving through a winding microfluidic channel. Previously, scaling arguments for chaotic mixing have been described for a flow that reduces striation length by stretching, folding, and reorienting the fluid in a manner similar to that of the baker's transformation. The experimentally observed flow patterns within droplets (or plugs) resembled the baker's transformation. Therefore, the ideas described in the literature could be applied to mixing in droplets to obtain the scaling argument for the dependence of the mixing time, t~(aw/U)log(Pe), where w [m] is the cross-sectional dimension of the microchannel, a is the dimensionless length of the plug measured relative to w, U [m s(-1)] is the flow velocity, Pe is the Péclet number (Pe=wU/D), and D [m(2)s(-1)] is the diffusion coefficient of the reagent being mixed. Experiments were performed to confirm the scaling argument by varying the parameters w, U, and D. Under favorable conditions, submillisecond mixing has been demonstrated in this system.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Analysis of chaotic mixing in plugs moving in meandering microchannels.Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2011 Dec;84(6 Pt 2):066309. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.84.066309. Epub 2011 Dec 12. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2011. PMID: 22304192
-
Numerical Modelling of Mixing in a Microfluidic Droplet Using a Two-Phase Moving Frame of Reference Approach.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Apr 30;13(5):708. doi: 10.3390/mi13050708. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35630175 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic systems for chemical kinetics that rely on chaotic mixing in droplets.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2004 May 15;362(1818):1087-104. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2003.1364. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2004. PMID: 15306486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidic baker's transformation device for three-dimensional rapid mixing.Lab Chip. 2011 Oct 7;11(19):3356-60. doi: 10.1039/c1lc20342h. Epub 2011 Aug 16. Lab Chip. 2011. PMID: 21845274
-
Design and simulation of the micromixer with chaotic advection in twisted microchannels.Lab Chip. 2003 May;3(2):77-81. doi: 10.1039/b211091a. Epub 2003 Apr 17. Lab Chip. 2003. PMID: 15100786
Cited by
-
Microfluidic transport in microdevices for rare cell capture.Electrophoresis. 2012 Nov;33(21):3133-42. doi: 10.1002/elps.201200263. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Electrophoresis. 2012. PMID: 23065634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a Microfluidic Platform for Trace Lipid Analysis.Metabolites. 2021 Feb 24;11(3):130. doi: 10.3390/metabo11030130. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 33668377 Free PMC article.
-
Droplet Microfluidics for Food and Nutrition Applications.Micromachines (Basel). 2021 Jul 23;12(8):863. doi: 10.3390/mi12080863. Micromachines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34442486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study of flow behaviors of droplet merging and splitting in microchannels using Micro-PIV measurement.Microfluid Nanofluidics. 2017 Apr;21(4):66. doi: 10.1007/s10404-017-1902-y. Epub 2017 Mar 27. Microfluid Nanofluidics. 2017. PMID: 28890680 Free PMC article.
-
Droplet and Particle Generation on Centrifugal Microfluidic Platforms: A Review.Micromachines (Basel). 2020 Jun 22;11(6):603. doi: 10.3390/mi11060603. Micromachines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32580516 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Song H, Tice JD, Ismagilov RF. Angew Chem, Int Ed Engl. 2003;42:768. - PubMed
-
- Beebe DJ, Mensing GA, Walker GM. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2002;4:261. - PubMed
-
- Ottino JM. The Kinematics of Mixing: Stretching, Chaos, and Transport. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: 1989.
-
- Aref H. J Fluid Mech. 1984;143:1.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
