Magnetic resonance imaging of the coronary arteries
- PMID: 17940671
- PMCID: PMC4170228
Magnetic resonance imaging of the coronary arteries
Abstract
Despite progress in prevention and early diagnosis, coronary artery disease (CAD) remains one of the leading causes of mortality in the world. For many years, invasive X-ray coronary angiography has been the method of choice for the diagnosis of significant CAD. However, up to 40% of patients referred for elective X-ray coronary angiography have no clinically significant stenoses. These patients still remain subjected to the potential risks of X-ray angiography. As an alternative, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is currently one of the most promising techniques for noninvasive imaging of the coronary arteries. Over the past two decades, many technical developments have been implemented that have led to major improvements in coronary MRI. Nowadays, both anatomical and functional information can be obtained with high temporal and spatial resolution and good image quality. In this review we will discuss the technical foundations and current status of clinical coronary MRI, and some potential future applications.
Figures


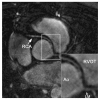

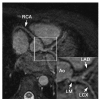

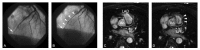
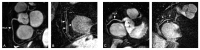
References
-
- Thom T, Haase N, Rosamond W, Howard VJ, Rumsfeld J, Manolio T. et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics − 2006 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2006;113:e85–e151. - PubMed
-
- Mackay J, Mensah GA. The Atlas of Heart Disease and Stroke. 1st edn. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2004.
-
- Kim WY, Danias PG, Stuber M, Flamm SD, Plein S, Nagel E. et al. Coronary magnetic resonance angiography for the detection of coronary stenoses. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:1863–1869. - PubMed
-
- Budoff MJ, Georgiou D, Brody A, Agatston AS, Kennedy J, Wolfkiel C. et al. Ultrafast computed tomography as a diagnostic modality in the detection of coronary artery disease: a multicenter study. Circulation. 1996;93:898–904. - PubMed
-
- Runge VM. Safety of approved MR contrast media for intravenous injection. J Magn Reson Imag. 2000;12:205–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

