Results of operative treatment of acetabular fractures from the Third World--how local factors affect the outcome
- PMID: 17940767
- PMCID: PMC2899060
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-007-0461-3
Results of operative treatment of acetabular fractures from the Third World--how local factors affect the outcome
Abstract
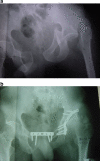
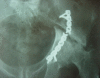
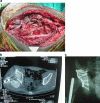
The objective of this study was to assess the outcome of operations on acetabular fractures from a developing country in the presence of locally available facilities. Sixty-three acetabular fractures were assessed at an average follow up of 52.94 months after operation. Twenty-six patients operated upon in the first three years and 37 operated thereafter were separately studied to discover the effect of the learning curve. Regarding the fractures, 47 of 63 (74.6%) had excellent/good results (Harris Hip Score>80). The complications included broken drill bit in eight patients (12.69%), deep infection and heterotopic ossification in five patients (7.93%), avascular necrosis and sciatic nerve palsy in two patients (3.17%) and implant failure in one patient (1.58%). The results collected during the learning curve were inferior in the complex fractures (p value<0.001). Complications were common in patients opting for local implants and in those operated after over 2 weeks delay.
Le but de ce travail est d’évaluer le traitement des fractures de l’accétabulum dans un pays développé. Matériel et méthode : 63 fractures de l’accétabulum ont été suivies en moyenne pendant 52,94 mois. 26 patients ont été opérés dans les trois premières années de notre expérience et les 37 autres patients opérés trois ans après que nous ayons commencé ce type de traitement, ceci afin d’évaluer de façon séparée les effets de notre courbe d’apprentissage. 47 sur 63 (74,6%) ont eu un excellent/bon résultat avec un score de Harris supérieur à 80. Les complications ont été les suivantes : 8 fractures de mèches (12,69%), 5 infections profondes (7,93%) et 7 ossifications hétérotypiques (7,93%), 2 nécroses de la tête fémorale et 2 paralysies sciatiques (3,17%) une dans chaque groupe. Enfin, un débricolage chez un patient (1,58%). Les résultats selon la courbe d’apprentissage sont moins bons dans des fractures complexes (p < 0.001) en début de pratique. Les complications sont plus habituelles chez les patients ayant bénéficié de la mise en place d’implants ou chez ceux opérés après 2 semaines de délai.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Two to twenty-year survivorship of the hip in 810 patients with operatively treated acetabular fractures.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012 Sep 5;94(17):1559-67. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.K.00444. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012. PMID: 22992846
-
[Total hip arthroplasty for treatment of acute acetabular fracture in elderly patients].Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2007 Dec;93(8):818-27. doi: 10.1016/s0035-1040(07)78465-9. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2007. PMID: 18166954 French.
-
Operative treatment of acetabular fractures through the extensile Henry approach.J Trauma. 1999 Feb;46(2):255-60. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199902000-00010. J Trauma. 1999. PMID: 10029030
-
Total hip arthroplasty following acetabular fracture.Orthopedics. 1999 Sep;22(9):837-9. doi: 10.3928/0147-7447-19990901-14. Orthopedics. 1999. PMID: 10507340 Review. No abstract available.
-
Management of neglected acetabular fractures.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2015 Aug;41(4):343-8. doi: 10.1007/s00068-014-0462-z. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2015. PMID: 26037994 Review.
Cited by
-
A Neglected Fracture of Acetabulum Treated With Total Hip Replacement.Cureus. 2024 Jun 6;16(6):e61778. doi: 10.7759/cureus.61778. eCollection 2024 Jun. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38975433 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstruction of unfixable comminuted posterior wall acetabular fractures with autologous bone graft: A systematic review.J Orthop. 2024 Oct 24;63:21-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2024.10.034. eCollection 2025 May. J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39530045 Review.
-
A safe technique of anterior column lag screw fixation in acetabular fractures.Int Orthop. 2012 Nov;36(11):2333-40. doi: 10.1007/s00264-012-1661-z. Epub 2012 Sep 23. Int Orthop. 2012. PMID: 23001195 Free PMC article.
-
Systems issues limiting acute fracture care delivery at a tertiary care hospital in Northern Tanzania.Pan Afr Med J. 2024 May 29;48:29. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2024.48.29.41286. eCollection 2024. Pan Afr Med J. 2024. PMID: 39220554 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical results of acetabular fracture treatment with hybrid fixation by anterior and posterior approach : A minimally invasive technique.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2024 Oct;136(19-20):556-561. doi: 10.1007/s00508-023-02277-2. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2024. PMID: 37815673
References
-
- Bosse MJ, Poka A, Reinert CM, Ellwanger F, Slawson R, McDevitt ER. Heterotopic ossification as a complication of acetabular fracture. Prophylaxis with low-dose irradiation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988;70(8):1231–1237. - PubMed
-
- Brooker AF, Bowerman JW, Robinson RA, Riley LH. Ectopic ossification following total hip replacement. Incidence and a method of classification. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973;55(8):1629–1632. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

