A computer-controlled ultrasound pulser-receiver system for transskull fluid detection using a shear wave transmission technique
- PMID: 17941383
- PMCID: PMC2186207
- DOI: 10.1109/tuffc.2007.461
A computer-controlled ultrasound pulser-receiver system for transskull fluid detection using a shear wave transmission technique
Abstract
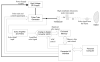
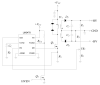
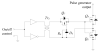
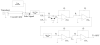
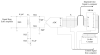
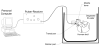
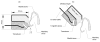
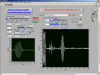
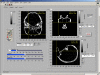
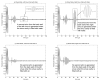
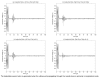
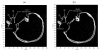
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the performance of a computer-controlled ultrasound pulser-receiver system incorporating a shear mode technique for transskull fluid detection. The presence of fluid in the sinuses of an ex vivo human skull was examined using a pulse-echo method by transmitting an ultrasound beam through the maxilla bone toward the back wall on the other side of the sinus cavity. The pulser was programmed to generate bipolar pulse trains with 5 cycles at a frequency of 1 MHz, repetition frequency of about 20 Hz, and amplitude of 100 V to drive a 1-MHz piezoelectric transducer. Shear and longitudinal waves in the maxilla bone were produced by adjusting the bone surface incident angle to 45 degrees and 0 degrees, respectively. Computer tomography (CT) scans of the skull were performed to verify the ultrasound experiment. Using the shear mode technique, the echo waveform clearly distinguishes the presence of fluid, and the estimated distance of the ultrasound traveled in the sinus is consistent with the measurement from the CT images. Contrarily, using the longitudinal mode, no detectable back wall echo was observed under the same conditions. As a conclusion, this study demonstrated that the proposed pulser-receiver system with the shear mode technique is promising for transskull fluid detecting, such as mucus in a sinus.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transcranial shear-mode ultrasound: assessment of imaging performance and excitation techniques.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2009 May;28(5):763-74. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2008.2012017. Epub 2009 Jan 13. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2009. PMID: 19150789
-
High frame rate imaging system for limited diffraction array beam imaging with square-wave aperture weightings.IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2006 Oct;53(10):1796-812. doi: 10.1109/tuffc.2006.112. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2006. PMID: 17036788
-
Front-end receiver electronics for a matrix transducer for 3-D transesophageal echocardiography.IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2012 Jul;59(7):1500-12. doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2012.2350. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2012. PMID: 22828845
-
Integration of 2D CMUT arrays with front-end electronics for volumetric ultrasound imaging.IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2008 Feb;55(2):327-42. doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2008.652. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2008. PMID: 18334340
-
Enhanced ultrasound transmission through the human skull using shear mode conversion.J Acoust Soc Am. 2004 Mar;115(3):1356-64. doi: 10.1121/1.1645610. J Acoust Soc Am. 2004. PMID: 15058357
Cited by
-
Driving circuitry for focused ultrasound noninvasive surgery and drug delivery applications.Sensors (Basel). 2011;11(1):539-56. doi: 10.3390/s110100539. Epub 2011 Jan 7. Sensors (Basel). 2011. PMID: 22346589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An intraoperative brain shift monitor using shear mode transcranial ultrasound: preliminary results.J Ultrasound Med. 2009 Feb;28(2):191-203. doi: 10.7863/jum.2009.28.2.191. J Ultrasound Med. 2009. PMID: 19168769 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Systems and Technologies: State-of-the-Art Applications, Opportunities, and Challenges.IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2020;13:325-339. doi: 10.1109/RBME.2019.2908940. Epub 2019 Apr 2. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2020. PMID: 30951478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A PVDF receiver for ultrasound monitoring of transcranial focused ultrasound therapy.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2010 Sep;57(9):2286-94. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2010.2050483. Epub 2010 May 27. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2010. PMID: 20515709 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Desrosiers M, Klossek JM, Benninger M. Management of Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis: Current Issues and Future Perspectives. International Journal of Clinical Practice. 2006 Feb;60:190–200. - PubMed
-
- Gonzales R, Bartlett JG, Besser RE, Cooper RJ, Hickner JM, Hoffman JR, Sande MA. Principles of appropriate antibiotic use for treatment of acute respiratory tract infections in adults: background, specific aims, and methods. Annals of internal medicine. 2001 March;134:479–486. - PubMed
-
- Winstead W. Rhinosinusitis. Primary Care; Clinics in Office Practice. 2003;30:137–154. - PubMed
-
- Garau J, Dagan R. Accurate Diagnosis and Appropriate Treatment of Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis, Minimizing Bacterial Resistance. Clinical therapeutics. 2003 July;25:1936–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

