Structural reorganisation and potential toxicity of oligomeric species formed during the assembly of amyloid fibrils
- PMID: 17941703
- PMCID: PMC1976335
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030173
Structural reorganisation and potential toxicity of oligomeric species formed during the assembly of amyloid fibrils
Abstract
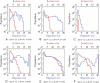
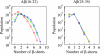
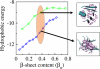
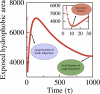
Increasing evidence indicates that oligomeric protein assemblies may represent the molecular species responsible for cytotoxicity in a range of neurological disorders including Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. We use all-atom computer simulations to reveal that the process of oligomerization can be divided into two steps. The first is characterised by a hydrophobic coalescence resulting in the formation of molten oligomers in which hydrophobic residues are sequestered away from the solvent. In the second step, the oligomers undergo a process of reorganisation driven by interchain hydrogen bonding interactions that induce the formation of beta sheet rich assemblies in which hydrophobic groups can become exposed. Our results show that the process of aggregation into either ordered or amorphous species is largely determined by a competition between the hydrophobicity of the amino acid sequence and the tendency of polypeptide chains to form arrays of hydrogen bonds. We discuss how the increase in solvent-exposed hydrophobic surface resulting from such a competition offers an explanation for recent observations concerning the cytotoxicity of oligomeric species formed prior to mature amyloid fibrils.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
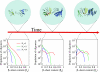
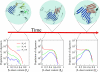
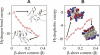

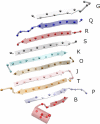
References
-
- Selkoe DJ. Folding proteins in fatal ways. Nature. 2003;426:900–904. doi: 10.1038/nature02264. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature02264. Accessed 8 August 2007. - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Roberson ED, Mucke L. 100 years and counting: Prospects for defeating Alzheimer disease. Science. 2006;314:781–784. doi: 10.1126/science.1132813. http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1132813. Accessed 8 August 2007. - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lansbury PT, Lashuel HA. A century-old debate on protein aggregation and neurodegeneration enters the clinic. Nature. 2006;443:774–779. doi: 10.1038/nature05290. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature05290. Accessed 8 August 2007. - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dobson CM. Protein misfolding, evolution and disease. Trends Biochem Sci. 1999;24:329–332. - PubMed
-
- Dobson CM. Protein folding and misfolding. Nature. 2003;426:884–890. doi: 10.1038/nature02261. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature02261. Accessed 8 August 2007. - DOI - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

