Inhibitors of pathogen intercellular signals as selective anti-infective compounds
- PMID: 17941706
- PMCID: PMC2323289
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030126
Inhibitors of pathogen intercellular signals as selective anti-infective compounds
Abstract
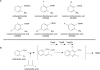
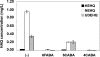
Long-term antibiotic use generates pan-resistant super pathogens. Anti-infective compounds that selectively disrupt virulence pathways without affecting cell viability may be used to efficiently combat infections caused by these pathogens. A candidate target pathway is quorum sensing (QS), which many bacterial pathogens use to coordinately regulate virulence determinants. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa MvfR-dependent QS regulatory pathway controls the expression of key virulence genes; and is activated via the extracellular signals 4-hydroxy-2-heptylquinoline (HHQ) and 3,4-dihydroxy-2-heptylquinoline (PQS), whose syntheses depend on anthranilic acid (AA), the primary precursor of 4-hydroxy-2-alkylquinolines (HAQs). Here, we identified halogenated AA analogs that specifically inhibited HAQ biosynthesis and disrupted MvfR-dependent gene expression. These compounds restricted P. aeruginosa systemic dissemination and mortality in mice, without perturbing bacterial viability, and inhibited osmoprotection, a widespread bacterial function. These compounds provide a starting point for the design and development of selective anti-infectives that restrict human P. aeruginosa pathogenesis, and possibly other clinically significant pathogens.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

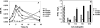
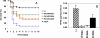

References
-
- Rasmussen TB, Givskov M. Quorum sensing inhibitors: A bargain of effects. Microbiology. 2006;152:895–904. - PubMed
-
- Rasmussen TB, Givskov M. Quorum-sensing inhibitors as anti-pathogenic drugs. Int J Med Microbiol. 2006;296:149–161. - PubMed
-
- Rossolini GM, Mantengoli E. Treatment and control of severe infections caused by multiresistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa . Clin Microbiol Infect. 2005;11(Suppl 4):17–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

