Topology correction of segmented medical images using a fast marching algorithm
- PMID: 17942182
- PMCID: PMC2128043
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2007.08.006
Topology correction of segmented medical images using a fast marching algorithm
Abstract
We present here a new method for correcting the topology of objects segmented from medical images. Whereas previous techniques alter a surface obtained from a binary segmentation of the object, our technique can be applied directly to the image intensities of a probabilistic or fuzzy segmentation, thereby propagating the topology for all isosurfaces of the object. From an analysis of topological changes and critical points in implicit surfaces, we derive a topology propagation algorithm that enforces any desired topology using a fast marching technique. The method has been applied successfully to the correction of the cortical gray matter/white matter interface in segmented brain images and is publicly released as a software plug-in for the MIPAV package.
Figures






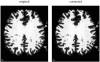
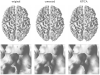
References
-
- van Essen DC, Maunsell HR. Two dimensional maps of the cerebral cortex. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1980;191:255–281. - PubMed
-
- Mangin J-F, Frouin V, Bloch I, Regis J, Lopez-Krahe J. From 3D magnetic resonance images to structural representations of the cortex topography using topology preserving deformations. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision. 1995;5:297–318.
-
- Han Xiao, Xu Chenyang, Prince Jerry L. A topology preserving level set method for geometric deformable models. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 2003;25(6):755–768.
-
- Bischoff Stefan, Kobbelt Leif. Sub-voxel topology control for level-set surfaces. Computer Graphics Forum. 2003;22(3):273–280.
-
- Bazin P-L, Pham DL. Topology-preserving tissue classification of magnetic resonance brain images. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. 2007;26(4):487–496. Special Issue on Computational Neuroanatomy. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

