Predictors of decision-making on the Iowa Gambling Task: independent effects of lifetime history of substance use disorders and performance on the Trail Making Test
- PMID: 17942206
- PMCID: PMC2292486
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bandc.2007.09.001
Predictors of decision-making on the Iowa Gambling Task: independent effects of lifetime history of substance use disorders and performance on the Trail Making Test
Abstract
Poor decision-making and executive function deficits are frequently observed in individuals with substance use disorders (SUDs), and executive deficits may contribute to poor decision-making in this population. This study examined the influence of lifetime history of an alcohol, cocaine, heroin, or polysubstance use disorder on decision-making as measured by the Iowa Gambling Task (IGT) after controlling for executive ability, demographic characteristics, and current substance use. Participants (131 with lifetime history of SUD and 37 controls) completed the IGT and two neuropsychological tests: the Trail Making Test and the Controlled Oral Word Association Test. Control participants performed significantly better than those with a lifetime SUD history on the IGT, but performance on the neuropsychological tests was comparable for the two groups. A lifetime SUD diagnosis was associated with performance on the IGT after controlling for covariates, and Trail Making Test performance was associated with IGT performance in both SUD and control participants.
Figures
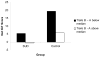

References
-
- Allen TJ, Moeller G, Rhoades HM, Cherek DR. Impulsivity and history of drug dependence. Drug and Alcohol Dependence. 1998;50:137–145. - PubMed
-
- Bates ME, Bowden SC, Barry D. Neurocognitive deficits associated with alcoholism: Implications for treatment. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology. 2002;10(3):193–212. - PubMed
-
- Bechara A. Decision making, impulse control and loss of willpower to resist drugs: A neurocognitive perspective. Nature Neuroscience. 2005;8:1458–1463. - PubMed
-
- Bechara A, Damasio AR, Damasio H, Anderson SW. Insensitivity to future consequences following damage to the human prefrontal cortex. Cognition. 1994;50:7–15. - PubMed
-
- Bechara S, Damasio H, Damasio AR. Emotion, decision making and the orbitofrontal cortex. Cerebral Cortex. 2000;10:295–307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 DA013444/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA 03510/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA003510/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA 018883/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA 13444/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA014618/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA 09241/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA018883/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR006192/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH061346/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH 60417/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH 61346/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA 016855/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA009241/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA021567/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA 14618/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060417/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA016855/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States

