Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp41 antibodies that mask membrane proximal region epitopes: antibody binding kinetics, induction, and potential for regulation in acute infection
- PMID: 17942537
- PMCID: PMC2224348
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00927-07
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp41 antibodies that mask membrane proximal region epitopes: antibody binding kinetics, induction, and potential for regulation in acute infection
Abstract
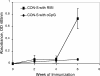
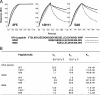
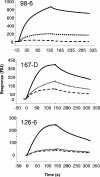
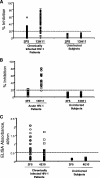
Two human monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) (2F5 and 4E10) against the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) envelope g41 cluster II membrane proximal external region (MPER) broadly neutralize HIV-1 primary isolates. However, these antibody specificities are rare, are not induced by Env immunization or HIV-1 infection, and are polyspecific and also react with lipids such as cardiolipin or phosphatidylserine. To probe MPER anti-gp41 antibodies that are produced in HIV-1 infection, we have made two novel murine MAbs, 5A9 and 13H11, against HIV-1 gp41 envelope that partially cross-blocked 2F5 MAb binding to Env but did not neutralize HIV-1 primary isolates or bind host lipids. Competitive inhibition assays using labeled 13H11 MAb and HIV-1-positive patient plasma samples demonstrated that cluster II 13H11-blocking plasma antibodies were made in 83% of chronically HIV-1 infected patients and were acquired between 5 to 10 weeks after acute HIV-1 infection. Both the mouse 13H11 MAb and the three prototypic cluster II human MAbs (98-6, 126-6, and 167-D) blocked 2F5 binding to gp41 epitopes to variable degrees; the combination of 98-6 and 13H11 completely blocked 2F5 binding. These data provide support for the hypothesis that in some patients, B cells make nonneutralizing cluster II antibodies that may mask or otherwise down-modulate B-cell responses to immunogenic regions of gp41 that could be recognized by B cells capable of producing antibodies like 2F5.
Figures


References
-
- Alam, S. M., C. A. Paleos, H-X. Liao, R. M. Scearce, J. Robinson, and B. F. Haynes. 2004. An inducible HIV-1 gp41 HR-2 peptide binding site on HIV-1 envelope gp120. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 20836-845. - PubMed
-
- Alam, S. M., M. McAdam, D. Boren, M. Rak, R. M. Scearce, F. Gao, Z. T. Camacho, D. Gewirth, G. Kelsoe, P. Chen, and B. F. Haynes. 2007. The role of antibody polyspecificity and lipid reactivity in binding of broadly neutralizing anti-HIV-1 envelope human monoclonal antibodies 2F5 and 4E10 to gp41 membrane proximal envelope epitopes. J. Immunol. 1784424-4435. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barin, F., M. F. McLane, J. S. Allan, T. H. Lee, J. E. Groopman, and M. Essex. 1985. Virus envelope protein of HTLV-III represents major target antigen for antibodies in AIDS patients. Science 2281094-1096. - PubMed
-
- Bowman, J. M. 1988. The prevention of Rh immunization. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2129-150. - PubMed
-
- Brenchley, J. M., T. W. Schacker, L. E. Ruff, D. A. Price, J. H. Taylor, G. J. Beilman, P. L. Nguyen, A. Khoruts, M. Larson, A. T. Haase, and D. C. Douek. 2004. CD4+ T cell depletion during all stages of HIV disease occurs predominantly in the gastrointestinal tract. J. Exp. Med. 200749-759. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

