Friend virus utilizes the BMP4-dependent stress erythropoiesis pathway to induce erythroleukemia
- PMID: 17942544
- PMCID: PMC2224407
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02487-06
Friend virus utilizes the BMP4-dependent stress erythropoiesis pathway to induce erythroleukemia
Abstract
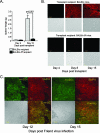
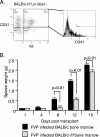
More than 50 years of genetic analysis has identified a number of host genes that are required for the expansion of infected cells during the progression of Friend-virus-induced erythroleukemia. In this report, we show that Friend virus induces the bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4)-dependent stress erythropoiesis pathway in the spleen, which rapidly amplifies target cells, propagating their infection and resulting in acute splenomegaly. This mechanism mimics the response to acute anemia, in which BMP4 expressed in the spleen drives the expansion of a specialized population of stress erythroid progenitors. Previously we demonstrated that these progenitors, termed stress BFU-E, are targets for Friend virus in the spleen (A. Subramanian, H. E. Teal, P. H. Correll, and R. F. Paulson, J. Virol. 79:14586-14594, 2005). Here, we extend those findings by showing that Friend virus infects two distinct populations of bone marrow cells. One population, when infected, differentiates into mature erythrocytes in an Epo-independent manner, while a second population migrates to the spleen after infection, where it induces BMP4 expression and acts as a reservoir of virus. The activation of the stress erythropoiesis pathway in the spleen by Friend virus results in the rapid expansion of stress BFU-E, providing abundant target cells for viral infection. These observations suggest a novel mechanism by which a virus induces a stress response pathway that amplifies target cells for the virus, leading to acute expansion of infected cells.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Self-renewal of leukemia stem cells in Friend virus-induced erythroleukemia requires proviral insertional activation of Spi1 and hedgehog signaling but not mutation of p53.Stem Cells. 2012 Feb;30(2):121-30. doi: 10.1002/stem.781. Stem Cells. 2012. PMID: 22083997 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation of the Lyn tyrosine kinase delays the progression of Friend virus induced erythroleukemia without affecting susceptibility.Leuk Res. 2006 Sep;30(9):1141-9. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2006.02.006. Epub 2006 Mar 9. Leuk Res. 2006. PMID: 16527351
-
Reduced Competitive Repopulation Capacity of Multipotential Hematopoietic Stem Cells in the Bone Marrow of Friend Virus-infected Fv2-resistant Mice.In Vivo. 2017 May-Jun;31(3):313-320. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11061. In Vivo. 2017. PMID: 28438857 Free PMC article.
-
Erythroleukaemia induction by the Friend spleen focus-forming virus.Baillieres Clin Haematol. 1995 Mar;8(1):225-47. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3536(05)80239-2. Baillieres Clin Haematol. 1995. PMID: 7663048 Review.
-
Friend erythroleukemia revisited.Blood. 2000 Dec 1;96(12):3675-80. Blood. 2000. PMID: 11090047 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
A detailed analysis of F-MuLV- and SFFV-infected cells in Friend virus-infected mice reveals the contribution of both F-MuLV- and SFFV-infected cells to the interleukin-10 host response.Retrovirology. 2022 Dec 16;19(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12977-022-00613-4. Retrovirology. 2022. PMID: 36527061 Free PMC article.
-
Selenium suppresses leukemia through the action of endogenous eicosanoids.Cancer Res. 2014 Jul 15;74(14):3890-901. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3694. Epub 2014 May 28. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24872387 Free PMC article.
-
GATA Factor-Regulated Samd14 Enhancer Confers Red Blood Cell Regeneration and Survival in Severe Anemia.Dev Cell. 2017 Aug 7;42(3):213-225.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.07.009. Dev Cell. 2017. PMID: 28787589 Free PMC article.
-
Friend Spleen Focus-Forming Virus Activates the Tyrosine Kinase sf-Stk and the Transcription Factor PU.1 to Cause a Multi-Stage Erythroleukemia in Mice.Viruses. 2010 Oct;2(10):2235-2257. doi: 10.3390/v2102235. Epub 2010 Oct 11. Viruses. 2010. PMID: 21994618 Free PMC article.
-
Self-renewal of leukemia stem cells in Friend virus-induced erythroleukemia requires proviral insertional activation of Spi1 and hedgehog signaling but not mutation of p53.Stem Cells. 2012 Feb;30(2):121-30. doi: 10.1002/stem.781. Stem Cells. 2012. PMID: 22083997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akashi, K., D. Traver, T. Miyamoto, and I. Weissman. 2000. A clonogenic common myeloid progenitor that gives rise to all myeloid lineages. Nature 404193-197. - PubMed
-
- Axelrad, A. 1969. Genetic and cellular basis of susceptibility or resistance to Friend leukemia virus infection in mice. Proc. Can. Cancer Conf. 8313-343. - PubMed
-
- Baumann, C. I., A. S. Bailey, W. Li, M. J. Ferkowicz, M. C. Yoder, and W. H. Fleming. 2004. PECAM-1 is expressed on hematopoietic stem cells throughout ontogeny and identifies a population of erythroid progenitors. Blood 1041010-1016. - PubMed
-
- Ben-David, Y., and A. Bernstein. 1991. Friend virus induced erythroleukemia and the multistage nature of cancer. Cell 66831-834. - PubMed
-
- Bennett, M., R. Steeves, G. Cudkowicz, E. Mirand, and L. Russell. 1968. Mutant Sl alleles of mice affect the susceptibility to Friend spleen focus forming virus. Science 162564-565. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

