Antiretroviral activity and Vif sensitivity of rhesus macaque APOBEC3 proteins
- PMID: 17942564
- PMCID: PMC2168863
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01760-07
Antiretroviral activity and Vif sensitivity of rhesus macaque APOBEC3 proteins
Abstract
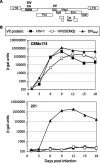
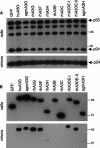
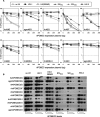
The inability of human immunodeficiency virus type 1(HIV-1) to replicate in rhesus macaque cells is in part due to the failure of HIV-1 Vif to counteract the restriction factor APOBEC3G. However, in this study we demonstrate that several rhesus macaque APOBEC3 (rhAPOBEC3) proteins are capable of inhibiting HIV-1 infectivity. There was considerable variation in the ability of a panel of Vif proteins to induce degradation of rhAPOBEC3 proteins, and mutations within HIV-1 Vif that render it capable of degrading rhAPOBEC3G did not confer activity against other antiviral rhAPOBEC3 proteins. These findings suggest that multiple APOBEC3 proteins can contribute to primate lentivirus species tropism.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human and rhesus APOBEC3D, APOBEC3F, APOBEC3G, and APOBEC3H demonstrate a conserved capacity to restrict Vif-deficient HIV-1.J Virol. 2011 Nov;85(21):11220-34. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05238-11. Epub 2011 Aug 10. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21835787 Free PMC article.
-
Mutational alteration of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vif allows for functional interaction with nonhuman primate APOBEC3G.J Virol. 2006 Jun;80(12):5984-91. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00388-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16731937 Free PMC article.
-
A single amino acid in human APOBEC3F alters susceptibility to HIV-1 Vif.J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 24;285(52):40785-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.173161. Epub 2010 Oct 22. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20971849 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between HIV-1 and APOBEC3 sub-family of proteins.Curr HIV Res. 2006 Oct;4(4):401-9. doi: 10.2174/157016206778560063. Curr HIV Res. 2006. PMID: 17073615 Review.
-
HIV-1 Vif versus the APOBEC3 cytidine deaminases: an intracellular duel between pathogen and host restriction factors.Mol Aspects Med. 2010 Oct;31(5):383-97. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2010.06.001. Epub 2010 Jun 9. Mol Aspects Med. 2010. PMID: 20538015 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Primate lentivirus capsid sensitivity to TRIM5 proteins.J Virol. 2008 Jul;82(13):6772-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00410-08. Epub 2008 Apr 16. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18417575 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 and HIV-2 Vif interact with human APOBEC3 proteins using completely different determinants.J Virol. 2014 Sep 1;88(17):9893-908. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01318-14. Epub 2014 Jun 18. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24942576 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the single deaminase domain APOBEC3A in virus restriction, retrotransposition, DNA damage and cancer.J Gen Virol. 2016 Jan;97(1):1-17. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000320. Epub 2015 Oct 20. J Gen Virol. 2016. PMID: 26489798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of APOBEC3 in hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and hepatocarcinogenesis.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):2074-2086. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1931640. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34043485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macaque-tropic human immunodeficiency virus type 1: breaking out of the host restriction factors.Front Microbiol. 2013 Jul 9;4:187. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00187. eCollection 2013. Front Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23847610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alce, T. M., and W. Popik. 2004. APOBEC3G is incorporated into virus-like particles by a direct interaction with HIV-1 Gag nucleocapsid protein. J. Biol. Chem. 279:34083-34086. - PubMed
-
- Bieniasz, P. D. 2004. Intrinsic immunity: a front-line defense against viral attack. Nat. Immunol. 5:1109-1115. - PubMed
-
- Cen, S., F. Guo, M. Niu, J. Saadatmand, J. Deflassieux, and L. Kleiman. 2004. The interaction between HIV-1 Gag and APOBEC3G. J. Biol. Chem. 279:33177-33184. - PubMed
-
- Conticello, S. G., R. S. Harris, and M. S. Neuberger. 2003. The Vif protein of HIV triggers degradation of the human antiretroviral DNA deaminase APOBEC3G. Curr. Biol. 13:2009-2013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

