p21 Inhibits Cdk1 in the absence of Cdk2 to maintain the G1/S phase DNA damage checkpoint
- PMID: 17942597
- PMCID: PMC2174178
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e07-06-0525
p21 Inhibits Cdk1 in the absence of Cdk2 to maintain the G1/S phase DNA damage checkpoint
Abstract
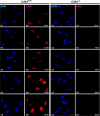
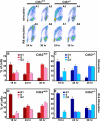
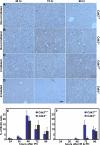
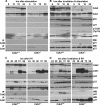
Cdk1 was proposed to compensate for the loss of Cdk2. Here we present evidence that this is possible due to premature translocation of Cdk1 from the cytoplasm to the nucleus in the absence of Cdk2. We also investigated the consequence of loss of Cdk2 on the maintenance of the G1/S DNA damage checkpoint. Cdk2(-/-) mouse embryonic fibroblasts in vitro as well as regenerating liver cells after partial hepatectomy (PH) in Cdk2(-/-) mice, arrest promptly at the G1/S checkpoint in response to gamma-irradiation due to activation of p53 and p21 inhibiting Cdk1. Furthermore re-entry into S phase after irradiation was delayed in Cdk2(-/-) cells due to prolonged and impaired DNA repair activity. In addition, Cdk2(-/-) mice were more sensitive to lethal irradiation compared to wild-type and displayed delayed resumption of DNA replication in regenerating liver cells. Our results suggest that the G1/S DNA damage checkpoint is intact in the absence of Cdk2, but Cdk2 is important for proper repair of the damaged DNA.
Figures

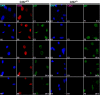
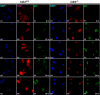

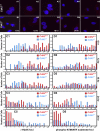
Similar articles
-
Requirements for p53 and the ATM gene product in the regulation of G1/S and S phase checkpoints.Oncogene. 1998 Feb 12;16(6):721-36. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201793. Oncogene. 1998. PMID: 9488036
-
An important role for CDK2 in G1 to S checkpoint activation and DNA damage response in human embryonic stem cells.Stem Cells. 2011 Apr;29(4):651-9. doi: 10.1002/stem.620. Stem Cells. 2011. PMID: 21319273
-
[E1A oncogene effect on the ability of p21(Waf1) to regulate G1/S arrest in E1A-expressing transformants following irradiation].Tsitologiia. 2005;47(12):1063-70. Tsitologiia. 2005. PMID: 16706194 Russian.
-
Pathways governing G1/S transition and their response to DNA damage.FEBS Lett. 2001 Feb 16;490(3):117-22. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(01)02114-7. FEBS Lett. 2001. PMID: 11223026 Review.
-
Genetic instability as a consequence of inappropriate entry into and progression through S-phase.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1995 Mar;14(1):59-73. doi: 10.1007/BF00690212. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1995. PMID: 7606822 Review.
Cited by
-
CDK-mediated RNF4 phosphorylation regulates homologous recombination in S-phase.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jun 23;43(11):5465-75. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv434. Epub 2015 May 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25948581 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analyses of gene expression profile reveal potential crucial roles of mitotic cell cycle and microtubule cytoskeleton in pulmonary artery hypertension.BMC Med Genomics. 2020 Jun 26;13(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s12920-020-00740-x. BMC Med Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32586319 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of radiation toxicity in transformed and non-transformed cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jul 31;14(8):15931-58. doi: 10.3390/ijms140815931. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23912235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of human BRCA1 variants in mouse ES cells allows functional analysis of BRCA1 mutations.J Clin Invest. 2009 Oct;119(10):3160-71. doi: 10.1172/JCI39836. Epub 2009 Sep 21. J Clin Invest. 2009. PMID: 19770520 Free PMC article.
-
A haploid genetic screen identifies the G1/S regulatory machinery as a determinant of Wee1 inhibitor sensitivity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Dec 8;112(49):15160-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1505283112. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26598692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed S. A., Gogal R. M., Jr, Walsh J. E. A new rapid and simple non-radioactive assay to monitor and determine the proliferation of lymphocytes: an alternative to [3H]-thymidine incorporation assay. J. Immunol. Methods. 1994;170:211–224. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht J. H., Meyer A. H., Hu M. Y. Regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21WAF1/Cip1/Sdi1 gene expression in hepatic regeneration. Hepatology. 1997;25:557–563. - PubMed
-
- Aleem E., Kiyokawa H., Kaldis P. Cdc2-cyclin E complexes regulate the G1/S phase transition. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005;7:831–836. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

