Copper-free click chemistry for dynamic in vivo imaging
- PMID: 17942682
- PMCID: PMC2040404
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0707090104
Copper-free click chemistry for dynamic in vivo imaging
Abstract
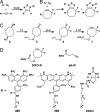
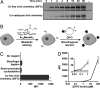
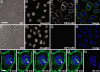
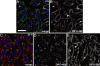
Dynamic imaging of proteins in live cells is routinely performed by using genetically encoded reporters, an approach that cannot be extended to other classes of biomolecules such as glycans and lipids. Here, we report a Cu-free variant of click chemistry that can label these biomolecules rapidly and selectively in living systems, overcoming the intrinsic toxicity of the canonical Cu-catalyzed reaction. The critical reagent, a substituted cyclooctyne, possesses ring strain and electron-withdrawing fluorine substituents that together promote the [3 + 2] dipolar cycloaddition with azides installed metabolically into biomolecules. This Cu-free click reaction possesses comparable kinetics to the Cu-catalyzed reaction and proceeds within minutes on live cells with no apparent toxicity. With this technique, we studied the dynamics of glycan trafficking and identified a population of sialoglycoconjugates with unexpectedly rapid internalization kinetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Giepmans BNG, Adams SR, Ellisman MH, Tsien RY. Science. 2006;312:217–224. - PubMed
-
- Griffin BA, Adams SR, Tsien RY. Science. 1998;281:269–272. - PubMed
-
- Carrico IS, Carlson BL, Bertozzi CR. Nat Chem Biol. 2007;3:321–322. - PubMed
-
- Chen I, Ting AY. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2005;16:35–40. - PubMed
-
- Prescher JA, Bertozzi CR. Nat Chem Biol. 2005;1:13–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

