Quantification of dynamic protein complexes using Renilla luciferase fragment complementation applied to protein kinase A activities in vivo
- PMID: 17942691
- PMCID: PMC2040481
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0704257104
Quantification of dynamic protein complexes using Renilla luciferase fragment complementation applied to protein kinase A activities in vivo
Abstract
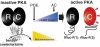
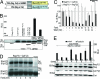
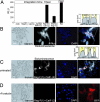
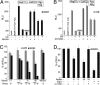
The G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily represents the most important class of pharmaceutical targets. Therefore, the characterization of receptor cascades and their ligands is a prerequisite to discovering novel drugs. Quantification of agonist-induced second messengers and downstream-coupled kinase activities is central to characterization of GPCRs or other pathways that converge on GPCR-mediated signaling. Furthermore, there is a need for simple, cell-based assays that would report on direct or indirect actions on GPCR-mediated effectors of signaling. More generally, there is a demand for sensitive assays to quantify alterations of protein complexes in vivo. We describe the development of a Renilla luciferase (Rluc)-based protein fragment complementation assay (PCA) that was designed specifically to investigate dynamic protein complexes. We demonstrate these features for GPCR-induced disassembly of protein kinase A (PKA) regulatory and catalytic subunits, a key effector of GPCR signaling. Taken together, our observations show that the PCA allows for direct and accurate measurements of live changes of absolute values of protein complex assembly and disassembly as well as cellular imaging and dynamic localization of protein complexes. Moreover, the Rluc-PCA has a sufficiently high signal-to-background ratio to identify endogenously expressed Galpha(s) protein-coupled receptors. We provide pharmacological evidence that the phosphodiesterase-4 family selectively down-regulates constitutive beta-2 adrenergic- but not vasopressin-2 receptor-mediated PKA activities. Our results show that the sensitivity of the Rluc-PCA simplifies the recording of pharmacological profiles of GPCR-based candidate drugs and could be extended to high-throughput screens to identify novel direct modulators of PKA or upstream components of GPCR signaling cascades.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Systematic Quantification of GPCR/cAMP-Controlled Protein Kinase A Interactions.Horm Metab Res. 2017 Apr;49(4):240-249. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-110791. Epub 2016 Aug 2. Horm Metab Res. 2017. PMID: 28427097
-
The cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor H-89 attenuates the bioluminescence signal produced by Renilla Luciferase.PLoS One. 2009 May 21;4(5):e5642. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005642. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19461967 Free PMC article.
-
In-vivo detection of binary PKA network interactions upon activation of endogenous GPCRs.Sci Rep. 2015 Jun 23;5:11133. doi: 10.1038/srep11133. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26099953 Free PMC article.
-
Luminescence- and Fluorescence-Based Complementation Assays to Screen for GPCR Oligomerization: Current State of the Art.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 17;20(12):2958. doi: 10.3390/ijms20122958. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31213021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation of G protein-coupled receptors: GPCR kinases in heart disease.Mol Interv. 2003 Aug;3(5):264-72. doi: 10.1124/mi.3.5.264. Mol Interv. 2003. PMID: 14993440 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetically encoded fluorescent biosensors illuminate kinase signaling in cancer.J Biol Chem. 2019 Oct 4;294(40):14814-14822. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV119.006177. Epub 2019 Aug 21. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31434714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Making connections for life: an in vivo map of the yeast interactome.HFSP J. 2008 Oct;2(5):244-50. doi: 10.2976/1.2969243. Epub 2008 Aug 13. HFSP J. 2008. PMID: 19404434 Free PMC article.
-
Luciferase protein complementation assays for bioluminescence imaging of cells and mice.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;680:29-43. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-901-7_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21153371 Free PMC article.
-
Asparagus IRX9, IRX10, and IRX14A Are Components of an Active Xylan Backbone Synthase Complex that Forms in the Golgi Apparatus.Plant Physiol. 2016 May;171(1):93-109. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.01919. Epub 2016 Mar 7. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26951434 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescent protein complementation assays: new tools to study G protein-coupled receptor oligomerization and GPCR-mediated signaling.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011 Jan 15;331(2):185-93. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2010.07.011. Epub 2010 Jul 21. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 20654687 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marinissen MJ, Gutkind JS. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001;22:368–376. - PubMed
-
- Dorsam RT, Gutkind JS. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:79–94. - PubMed
-
- Hopkins AL, Groom CR. Nat Rev. 2002;1:727–730. - PubMed
-
- Pierce KL, Premont RT, Lefkowitz RJ. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:639–650. - PubMed
-
- Jacoby E, Bouhelal R, Gerspacher M, Seuwen K. Chem Med Chem. 2006;1:761–782. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

