Activated vitamin D attenuates left ventricular abnormalities induced by dietary sodium in Dahl salt-sensitive animals
- PMID: 17942703
- PMCID: PMC2040477
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0611202104
Activated vitamin D attenuates left ventricular abnormalities induced by dietary sodium in Dahl salt-sensitive animals
Abstract
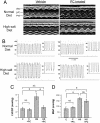
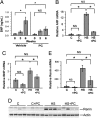
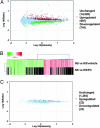
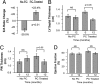
Observations in hemodialysis patients suggest a survival advantage associated with activated vitamin D therapy. Left ventricular (LV) structural and functional abnormalities are strongly linked with hemodialysis mortality. Here, we investigated whether paricalcitol (PC, 19-nor-1,25(OH)(2)D(2)), an activated vitamin D compound, attenuates the development of LV abnormalities in the Dahl salt-sensitive (DSS) rat and whether humans demonstrate comparable findings. Compared with DSS rats fed a high-salt (HS) diet (6% NaCl for 6 weeks), HS+PC was associated with lower heart and lung weights, reduced LV mass, posterior wall thickness and end diastolic pressures, and increased fractional shortening. Blood pressures did not significantly differ between the HS groups. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide levels, and cardiac mRNA expression of brain natriuretic peptide, atrial natriuretic factor, and renin were significantly reduced in the HS+PC animals. Microarray analyses revealed 45 specific HS genes modified by PC. In a retrospective pilot study of hemodialysis patients, PC-treated subjects demonstrated improved diastolic function and a reduction in LV septal and posterior wall thickness by echocardiography compared with untreated patients. In summary, PC attenuates the development of LV alterations in DSS rats, and these effects should be examined in human clinical trials.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The study was supported in part by Abbott Laboratories.
Figures
References
-
- Foley RN, Parfrey PS, Sarnak MJ. Am J Kidney Dis. 1998;32:S112–S119. - PubMed
-
- Parfrey PS, Foley RN, Harnett JD, Kent GM, Murray DC, Barre PE. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1996;11:1277–1285. - PubMed
-
- Teng M, Wolf M, Lowrie E, Ofsthun N, Lazarus JM, Thadhani R. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:446–456. - PubMed
-
- Teng M, Wolf M, Ofsthun MN, Lazarus JM, Hernan MA, Camargo CA, Jr, Thadhani R. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:1115–1125. - PubMed
-
- Pitts TO, Piraino BH, Mitro R, Chen TC, Segre GV, Greenberg A, Puschett JB. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988;67:876–881. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

